



Realignment - Vertical
A change in the vertical alignment of a road is often implicated in head-on, intersection and overtaking crashes.
Vertical road realignment may be used to:
- reduce grade (travelling down steep grades can cause brake failure, for heavy vehicles in particular, while travelling up steep grades must be done slowly in some vehicles, and can result in overtaking crashes and poor traffic flow).
- increase the radius of a crest for adequate sight distance (by “shaving” the top off of the crest)
- minimise vertical acceleration changes (for example, sag curves can be very uncomfortable for vehicle occupants
- address drainage problems (water can collect in sag curves, causing a safety problem).
Intersection approaches may be realigned vertically (or horizontally, or both) to improve sight distance. Realigning the road is costly and time consuming because it usually involves rebuilding a section of the road.
Benefits
Implementation issues
Benefits
- Reduced risk of head-on, intersection and overtaking crashes.
- Reduced risk of vehicle equipment failure (steep grades).
- More uniform traffic flow.
Implementation issues
- Vertical curve realignments require a lot of design and construction effort, and a lot of time and money. It is much better to design the road well before it is built than to rebuild it.
- Horizontal and vertical alignments should be considered together. Poor combinations of vertical and horizontal alignment can confuse drivers and lead to dangerous situations.
- Vertical realignment can result in existing side roads joining the main road at excessive gradient. For side roads joining from a lower height, this entails increased risk of collision due to slow turning manoeuvers at restart and visibility problems. For side roads joining from higher grounds, this entails increased risk of vehicles overrunning the stop line. Therefore, vertical realignment often requires concurrent treatment of side roads.
- Realignment can have significant environmental impacts due to increased footprints and earthworks.
The Star Rating Demonstrator is a freely available tool with the iRAP online software, ViDA. With the Star Rating Demonstrator, it is possible to explore the impact that this Safer Roads Treatment has on risk.
Treatment Summary
Costs | High |
Treatment life | 20 years + |
Potential casualty reduction | 10-25% |
Case Studies
Related Images
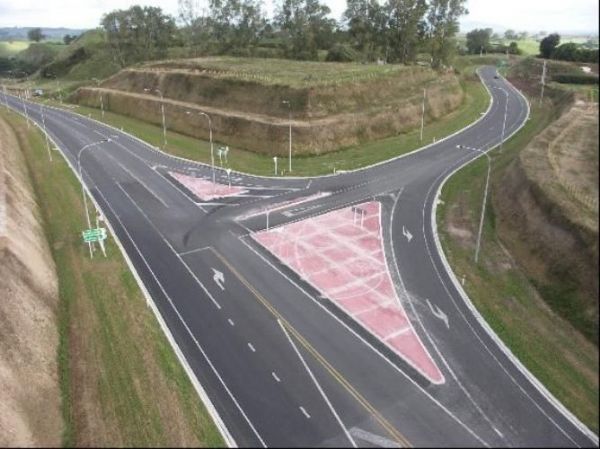 An upgraded intersection with protected turn lane, involving horizontal and vertical realignment. Image credit: ARRB Group
An upgraded intersection with protected turn lane, involving horizontal and vertical realignment. Image credit: ARRB Group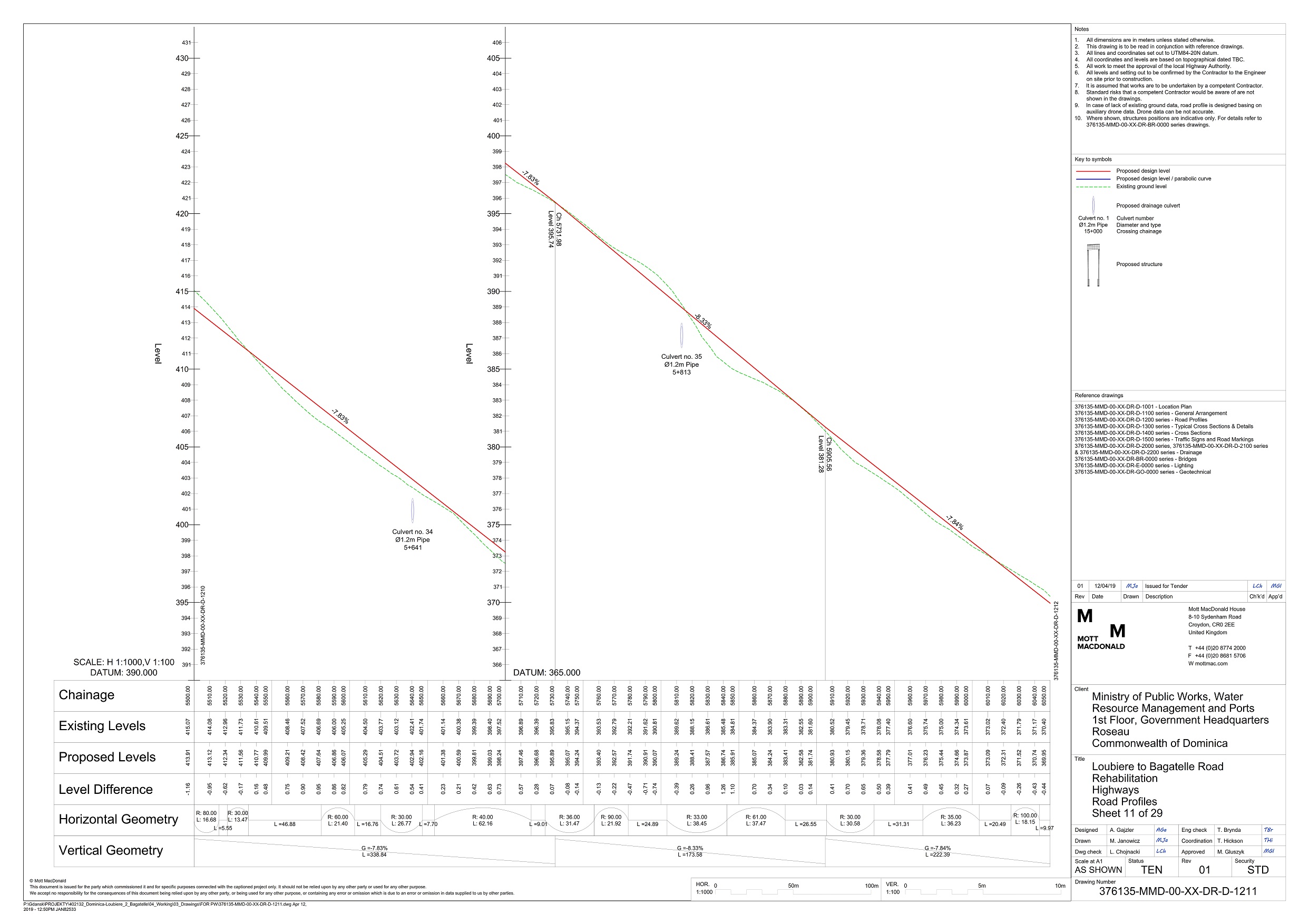 A design showing a planned vertical realignment of a road in Dominica. Image credit: Ministry of Public Works
A design showing a planned vertical realignment of a road in Dominica. Image credit: Ministry of Public Works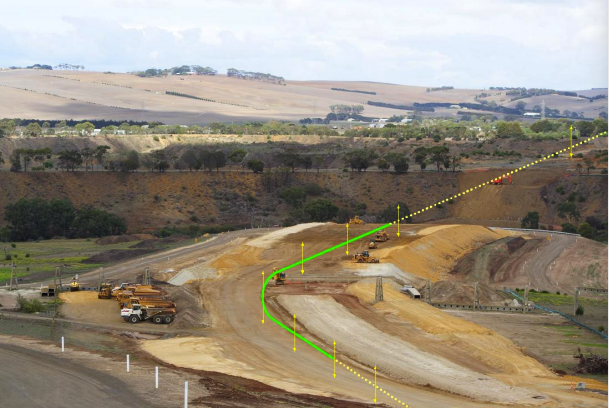 Example of vertical alignment - India. Image credit: Unknown
Example of vertical alignment - India. Image credit: Unknown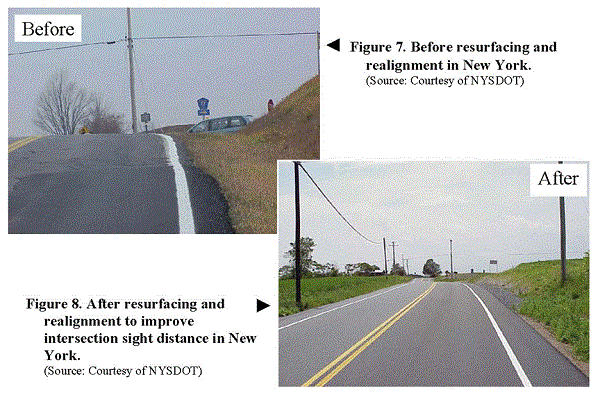 Before and after images of a location where alignment and pavement improvements were made in the USA. Image credit: FHWA and NYSDOT
Before and after images of a location where alignment and pavement improvements were made in the USA. Image credit: FHWA and NYSDOT










