



Motor Vehicle Standards
Some countries have legal requirements for the minimum safety standards of vehicles. This means that all new vehicles and all vehicles that are still on the road must meet this minimum set of safety standards to be sold and driven legally.
However, a large proportion of low and middle income countries don’t have standards that meet the minimum requirements recommended by the United Nations World Forum for the harmonization of vehicle regulations (WP.29) which are:
- 14: Seat belt anchorages.
- 16: Safety belts & restraints.
- 94: Frontal collision.
- 95: Lateral collision.
- 13H (GTR 8): Electronic stability control.
- 127 (GTR 9): Pedestrian protection.
- 44/129: Child restraints.
- 78 (GTR): Motorcycle ABS.
Some countries also require that vehicles are tested by trained inspectors at regular intervals to make sure that they continue to meet these standards.
Motor vehicle standards (including (Australian Design Rules, USA Federal motor vehicle safety standards and regulations and UN Regulations) cover requirements such as:
- controls
- displays
- rear view mirrors
- the order of gear shifting
- brake systems
- headlights, brake lights, blinkers (turning signals), backing lights
- tyre standard
- tyre rim standard
- safety glass for windows
- seatbelts and anchoring them correctly
- vehicle noise
- smoke/gas emissions.
Treatment Summary
Costs | Low |
Treatment life | 20 years + |
Potential casualty reduction | 60% or more |
Case Studies
Related Images
 Anti-Lock Brakes (ABS) for motorcycles. Image credit: Stop The Crash.
Anti-Lock Brakes (ABS) for motorcycles. Image credit: Stop The Crash. Electronic Stability Control (ESC). Image credit: Stop The Crash.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC). Image credit: Stop The Crash.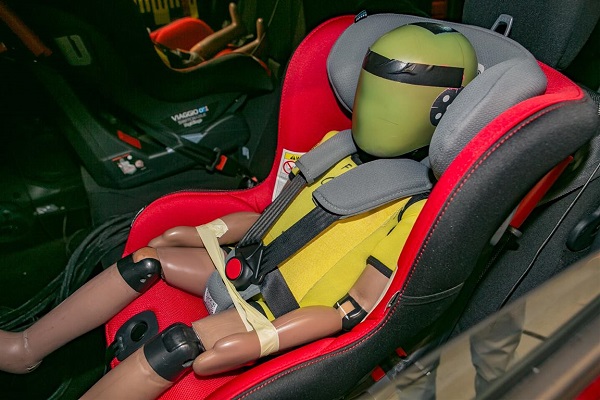 Child seats and restraints ready for crash testing. Image credit: LatinNCAP
Child seats and restraints ready for crash testing. Image credit: LatinNCAP Child seats and restraints ready for crash testing. Image credit: LatinNCAP
Child seats and restraints ready for crash testing. Image credit: LatinNCAP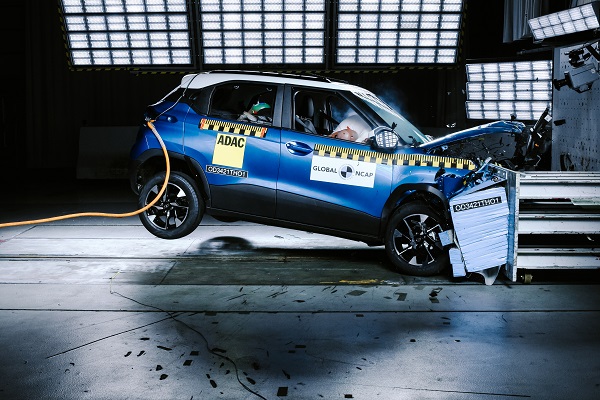 Airbag deploying during a crash test. Image credit: GlobalNCAP
Airbag deploying during a crash test. Image credit: GlobalNCAP Tyre Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) and tyre safety. Image credit: Stop The Crash.
Tyre Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) and tyre safety. Image credit: Stop The Crash.









