



Central Hatching - Wide Centrelines
Fewer head-on and overtaking crashes. Can remove turning vehicles from through traffic lanes, resulting in fewer rear-end and turning crashes and improved traffic flow. Improved delineation. Some reduction in speeds. Possible protection for pedestrians. Inexpensive.
If rumble strips, or other raised pavement devices are also used, the risk to motorcycles and pedestrians (trip hazard) must be considered. Coloured surfacing may be applied to the hatched area to further enhance the conspicuity of the treatment.
Treatment Summary
10-25% |
Case Studies

Central hatching median. This type of median decreased the likelihood of head-on collisions on undivided roads. Image credit: iRAP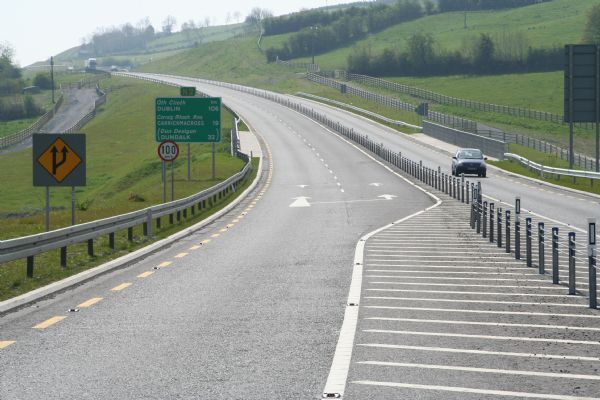 
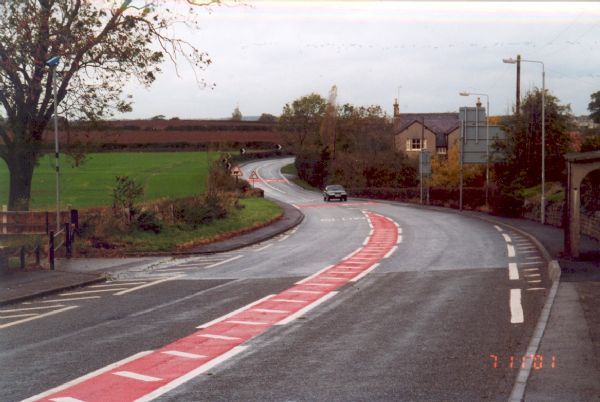
A divided road in Ireland with 2+1 lane configuration and wire-rope median barrier. Image credit: EuroRAP 
Road with central (ladder) hatching median in Perak, Malaysia. Image credit: MIROS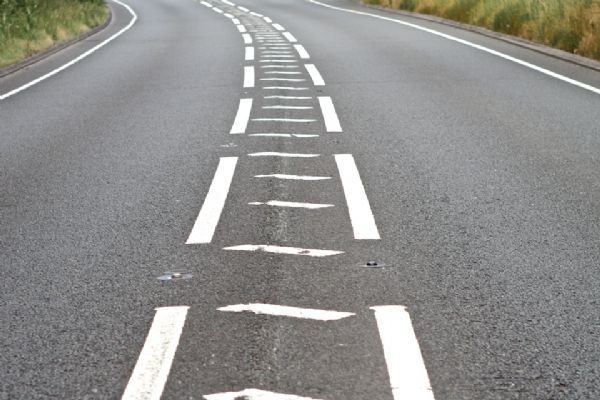 
Central (ladder) hatching on A21, UK. Image credit: Unknown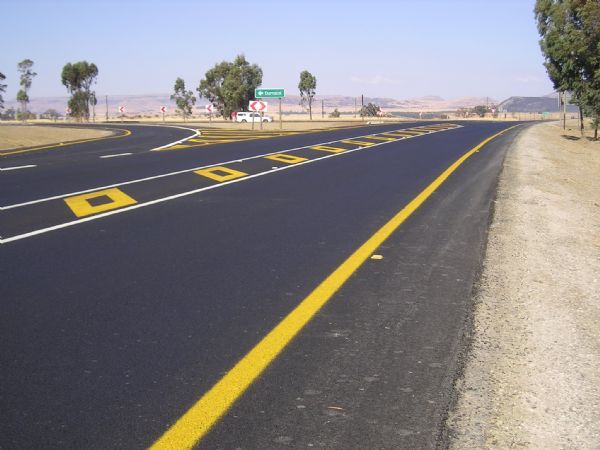 
Central hatching at an intersection in South Africa. Image credit: iRAP 
Central hatching in South America. Image credit: Doug Harwood 
Curve with central hatching median. Image credit: Kerala State Transport Project 
Good road surface South Africa. Image credit: iRAP 
Showing wide centreline treatment incorporating median rumble strips, Old Bruce Highway, Australia. Image credit: Unknown 
Pedestrian refuges, bicycle lanes, delineation and one-way road treatment. Image credit: Google Maps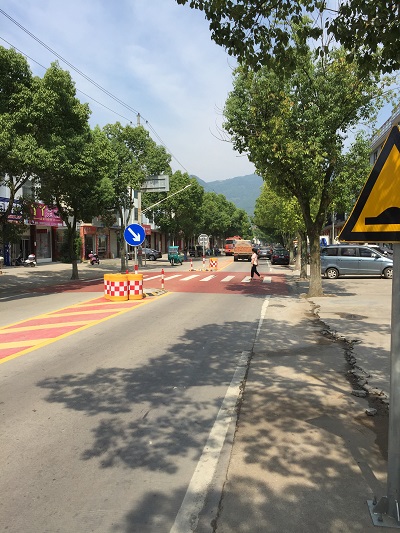 
Wide center line treatment on undivided road in QLD, Australia. Image credit: Ken Thomason 
Wide center line treatment on undivided road in QLD, Australia. Image credit: Ken Thomason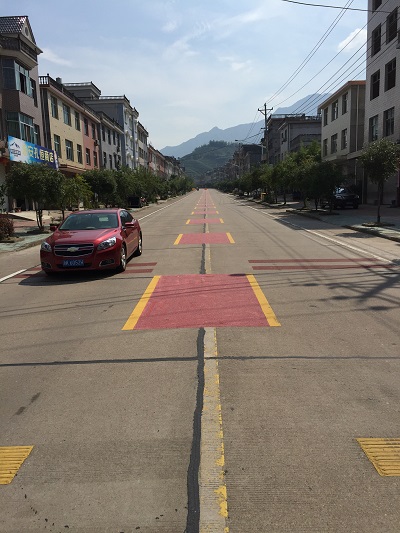 
Road with central hatching median in China. Image credit: Greg Smith










