



Pedestrian Crossing - Unsignalised
Most pedestrian crashes occur while the pedestrian is attempting to cross the road. A range of treatments can help pedestrians to cross safely, including the use of formal crossing points.
Unsignalised pedestrian crossings typically consist of signs and painted road markings (‘zebra crossings’).
Pedestrians are meant to have right of way over vehicles, but in many regions drivers do not stop for pedestrians. If this happens, unsignalised pedestrian crossings have few benefits and may actually be a hazard. These crossings are only suitable in situations with low traffic volumes and speeds.
Unsignalised pedestrian crossings may be unmarked and do not consist of strip markings. Pedestrians do not have priority and decide when it is safe to cross. The advantage is no delay to vehicles and only minor delay for pedestrians at light to moderate traffic volume. However, collisions could happen if pedestrians misjudge a safe gap while drivers do not expect to stop. Visually or mobility impaired pedestrians may also find it difficult to use these crossings.
Unsignalised pedestrian crossings may incorporate a raised feature (raised crossing) designed to slow the speed of approaching vehicles. The presence of such features should be clearly marked and advance warning provided. Various other safety devices can be included at crossings to improve safety, including traffic calming, refuge islands, advanced warning signs and pavement markings, street lighting, and flashing lights.
In all circumstances, unsignalised crossings should be highly conspicuous and visible to approach drivers. It is always desirable to reduce traffic speed on the approach and through the crossing area.
- Can help to reduce risk for pedestrians attempting to cross the road.
- Provides a clearly defined crossing point where pedestrians are ‘expected’.
- If combined with a raised platform type feature crossings can help to slow approaching traffic speeds.
- Reduced pedestrian crashes if installed at appropriate locations, and if pedestrian priority is enforced.
- Disruption to traffic flow is comparatively low.
- Unsignalised crossings are not suitable where traffic volumes or speeds are high.
- Unsignalised crossings could be more difficult to use for visually and mobility impaired pedestrians.
- On busy roads, usage of unsignalised crossings can be facilitated by regular gaps in the traffic stream created by upstream signalised intersections.
- Unsignalised crossings are not suitable where pedestrians need to cross two lanes in the same traffic direction, unless raised platforms are in place to slow down traffic.
- Traffic calming to reduce approach speed is always desirable for unsignalized crossings.
- Pedestrians will only use crossings located at, or very near, to where they want to cross. Pedestrian fencing can be used to encourage use of pedestrian crossings.
- Unmarked crossings could be appropriate for isolated and lightly used crossings so that pedestrians become more vigilant. However, such crossings should be very conspicuous for drivers and traffic calming to reduce approach speed should be in place.
- Consider incorporating a pedestrian refuge island where possible. Such islands should be at least 2.1m in width to accommodate all types of users.
- Through traffic must be able to see pedestrian crossing points in time to stop for them. Advance warning signs should be used if visibility is poor.
- Other high visibility devices (such as flashing lights) may also be used.
- Parking should be removed from near pedestrian crossings to provide adequate sight distance.
- The crossing will only be effective if other road users give way to pedestrians.
- Education and enforcement may be necessary to ensure pedestrians have priority.
- Consideration should be given to improving accessibility for the mobility impaired. This may include design features such as paved footpaths with sufficient width to accommodate wheelchairs, dropped kerbs at pedestrian crossing points and tactile paving.
The Star Rating Demonstrator is a freely available tool with the iRAP online software, ViDA. With the Star Rating Demonstrator, it is possible to explore the impact that this Safer Roads Treatment has on risk.
Treatment Summary
Costs | Low |
Treatment life | 1 year - 5 years |
Potential casualty reduction | 25-40% |
Case Studies
Related Images
 Marked pedestrian crossing facility with refuge island. Image credit: iStock
Marked pedestrian crossing facility with refuge island. Image credit: iStock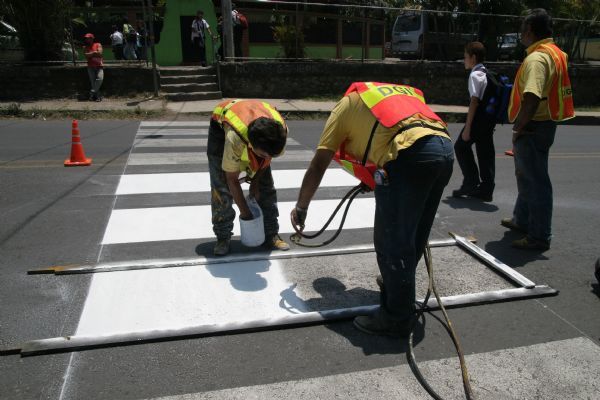 A pedestrian crossing being marked in Costa Rica. Image credit: Make Roads Safe
A pedestrian crossing being marked in Costa Rica. Image credit: Make Roads Safe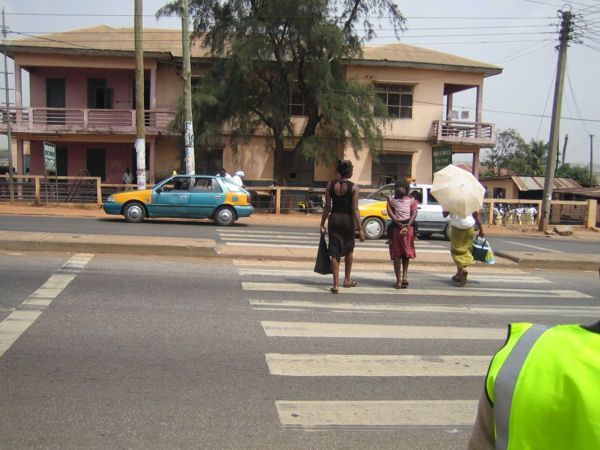 A pedestrian crossing facility with refuge island in Ghana. Image credit: John Fletcher
A pedestrian crossing facility with refuge island in Ghana. Image credit: John Fletcher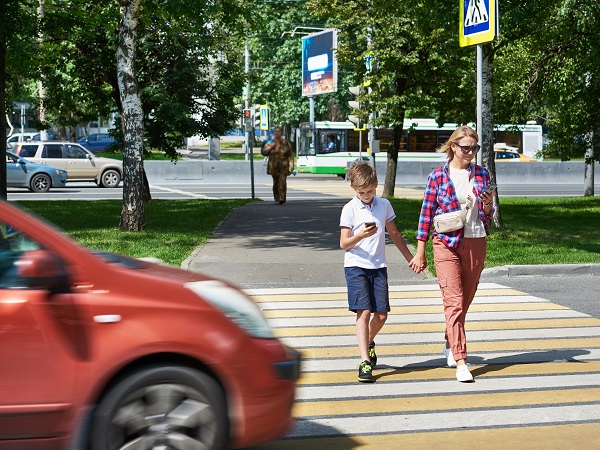 A potential crash involving mother and child pedestrians. Image credit: iStock
A potential crash involving mother and child pedestrians. Image credit: iStock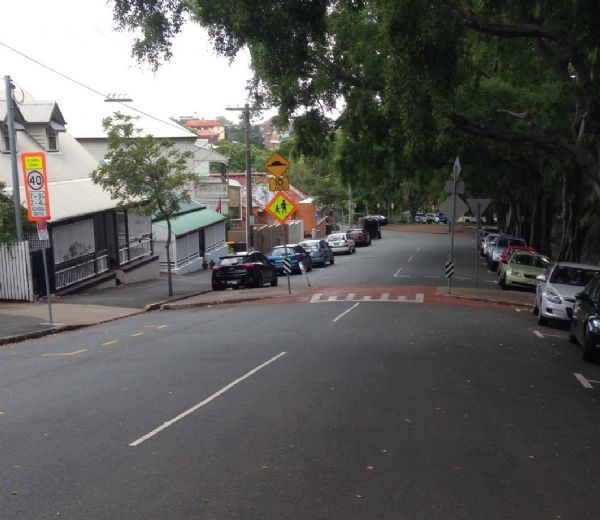 A raised pedestrian crossing with kerb build-out in a school zone in Brisbane, Australia. This is an effective traffic calming measure whilst providing a safe place to cross. Image credit: Luke Rogers
A raised pedestrian crossing with kerb build-out in a school zone in Brisbane, Australia. This is an effective traffic calming measure whilst providing a safe place to cross. Image credit: Luke Rogers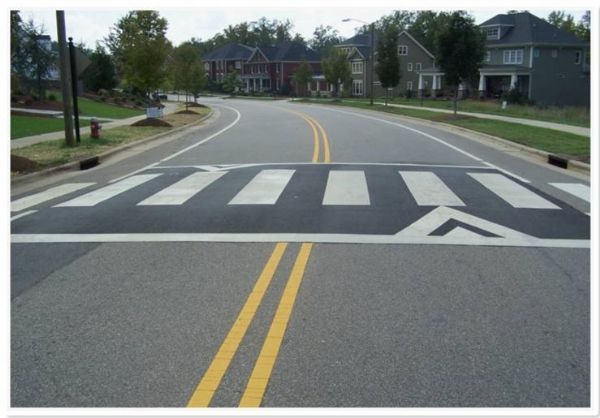 A raised pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Unknown
A raised pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Unknown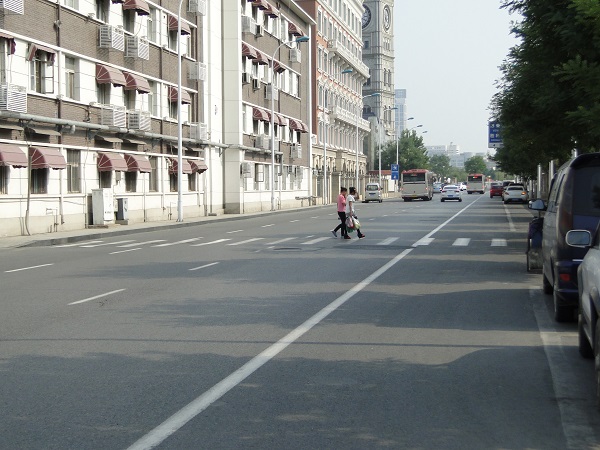 An unsignalised pedestrian crossing across four traffic lanes in China. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers
An unsignalised pedestrian crossing across four traffic lanes in China. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers Busy pedestrian crossing. Image credit: iStock
Busy pedestrian crossing. Image credit: iStock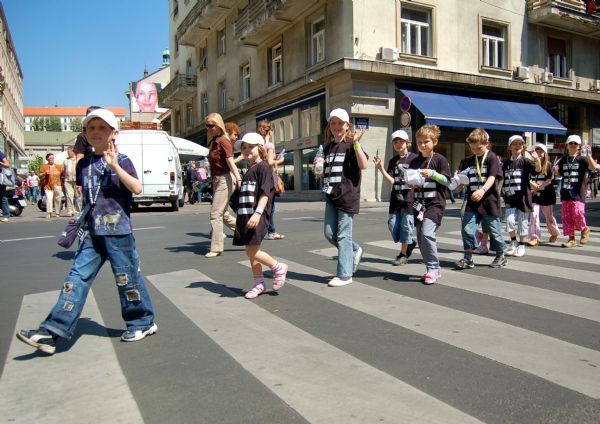 Children in Croatia using a pedestrian crossing. Image credit: Make Roads Safe
Children in Croatia using a pedestrian crossing. Image credit: Make Roads Safe City street with unsignalised pedestrian crossing in Madrid, Spain. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
City street with unsignalised pedestrian crossing in Madrid, Spain. Image credit: Alina Burlacu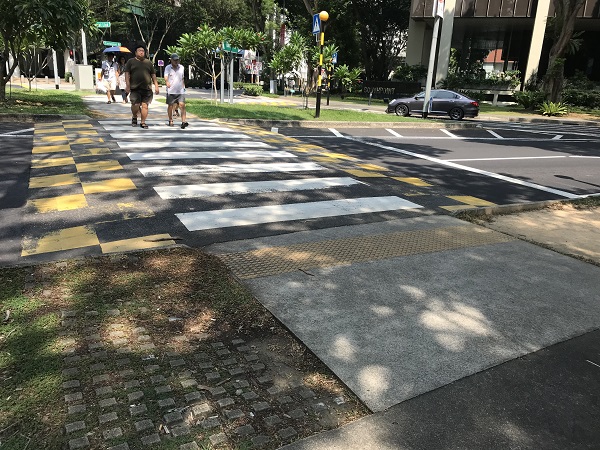 Raised pedestrian crossing in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Raised pedestrian crossing in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu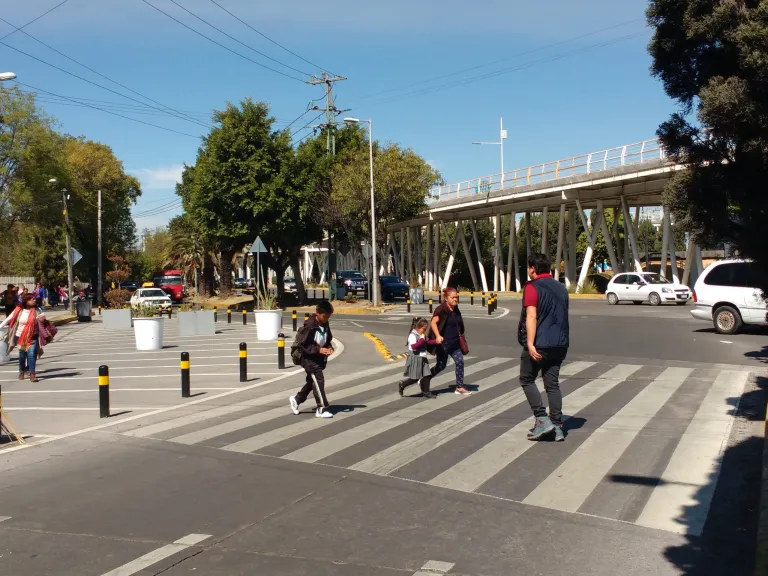 Pedestrian crossing and sidewalk at a school in Mexico. Image credit: ITDP
Pedestrian crossing and sidewalk at a school in Mexico. Image credit: ITDP 3-leg intersection with pedestrian facilities. Image credit: Kerala State Transport Project
3-leg intersection with pedestrian facilities. Image credit: Kerala State Transport Project Marked pedestrian crossing facility (Zebra marking). Image credit: Alain Rouiller
Marked pedestrian crossing facility (Zebra marking). Image credit: Alain Rouiller Pedestrian crossing facility with footpath, wide centreline and speed transverse markings to calm speed on a state highway in Kerala, India. Image credit: Kerala State Transport Project
Pedestrian crossing facility with footpath, wide centreline and speed transverse markings to calm speed on a state highway in Kerala, India. Image credit: Kerala State Transport Project Stop sign and sidewalk in United Arab Emirates. Image Credit: iRAP
Stop sign and sidewalk in United Arab Emirates. Image Credit: iRAP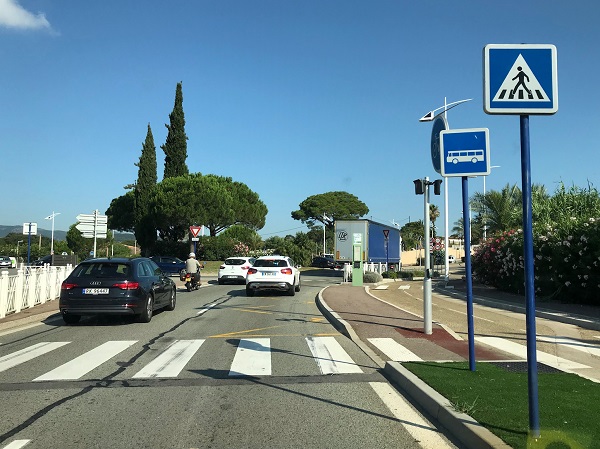 Pedestrian crossing in France. Image credit: iRAP
Pedestrian crossing in France. Image credit: iRAP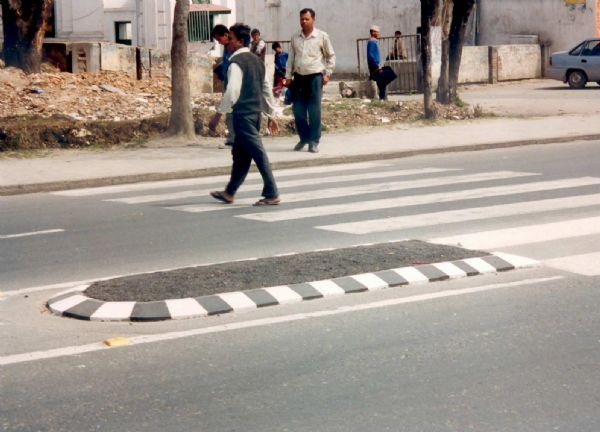 Pedestrian refuge island (overrunable) in Kathmandu. Image credit: Allan Jones
Pedestrian refuge island (overrunable) in Kathmandu. Image credit: Allan Jones Raised (table-top type) pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Alain Rouiller
Raised (table-top type) pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Alain Rouiller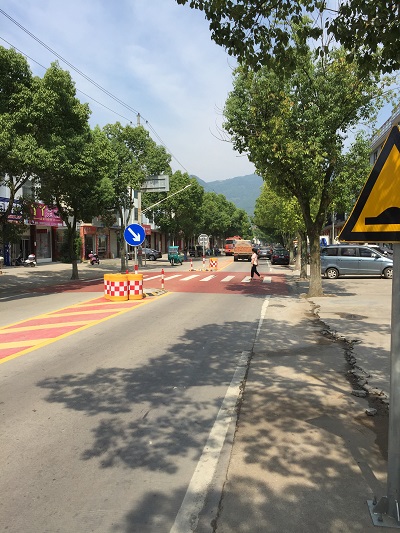 Raised pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Greg Smith
Raised pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Greg Smith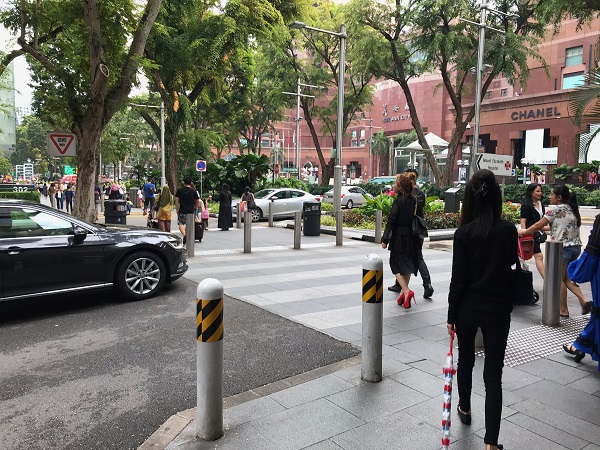 Raised pedestrian crossing facility in China. Image credit: Unknown
Raised pedestrian crossing facility in China. Image credit: Unknown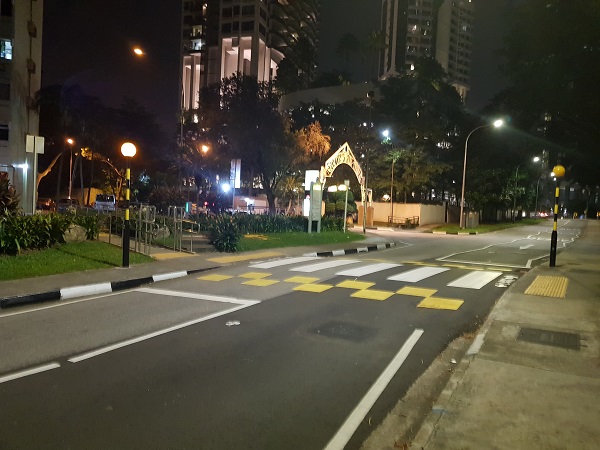 Raised pedestrian crossing in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Raised pedestrian crossing in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu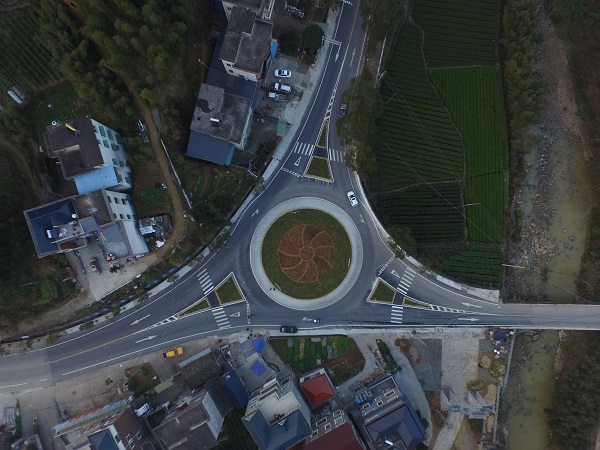 Roundabout with pedestrian crossing facility in China. Image credit: RIOH
Roundabout with pedestrian crossing facility in China. Image credit: RIOH School crossing improvements and Star Ratings. Image credit: Fundación Gonzalo Rodríguez
School crossing improvements and Star Ratings. Image credit: Fundación Gonzalo Rodríguez School crossing safety improvements in India. Image credit: TRAX
School crossing safety improvements in India. Image credit: TRAX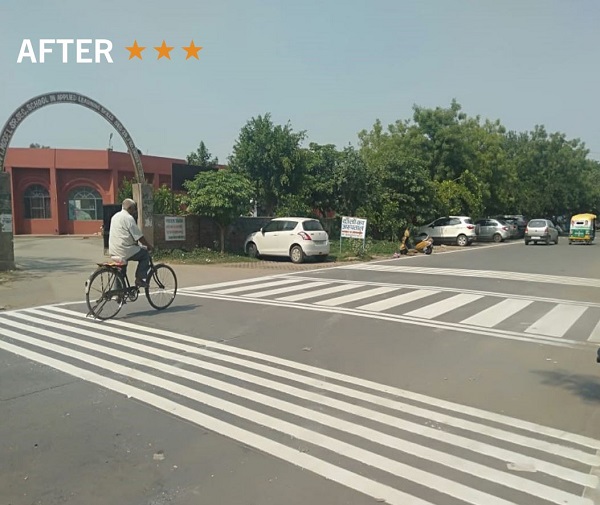 School crossing safety improvements in India. Image credit: TRAX
School crossing safety improvements in India. Image credit: TRAX School crossing safety improvements in India. Image credit: TRAX
School crossing safety improvements in India. Image credit: TRAX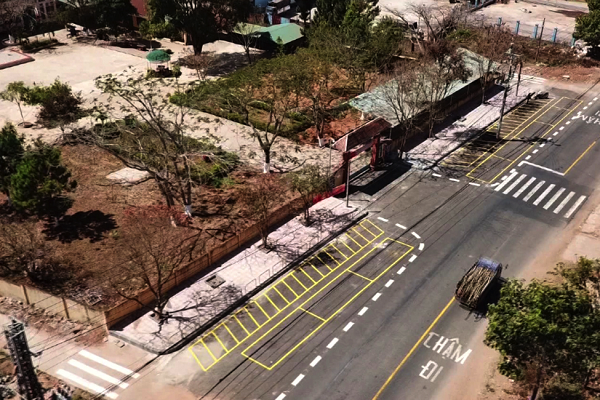 School safety improvements. Image credit: Asia Injury Prevention Foundation
School safety improvements. Image credit: Asia Injury Prevention Foundation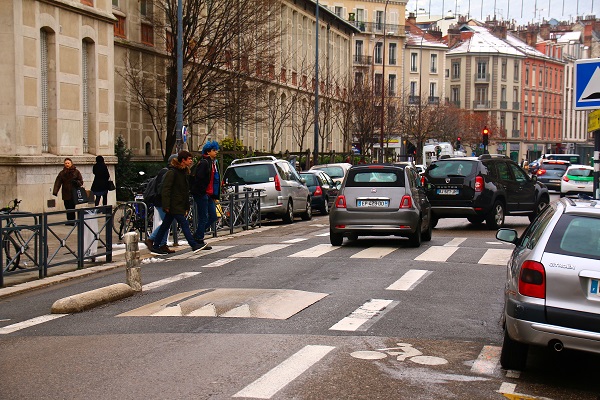 Pedestrians crossing the road, with traffic calming and pedestrian crossing. Image credit: RdA Suisse
Pedestrians crossing the road, with traffic calming and pedestrian crossing. Image credit: RdA Suisse Unmarked raised pedestrian crossing in Mexico. Image credit: iRAP
Unmarked raised pedestrian crossing in Mexico. Image credit: iRAP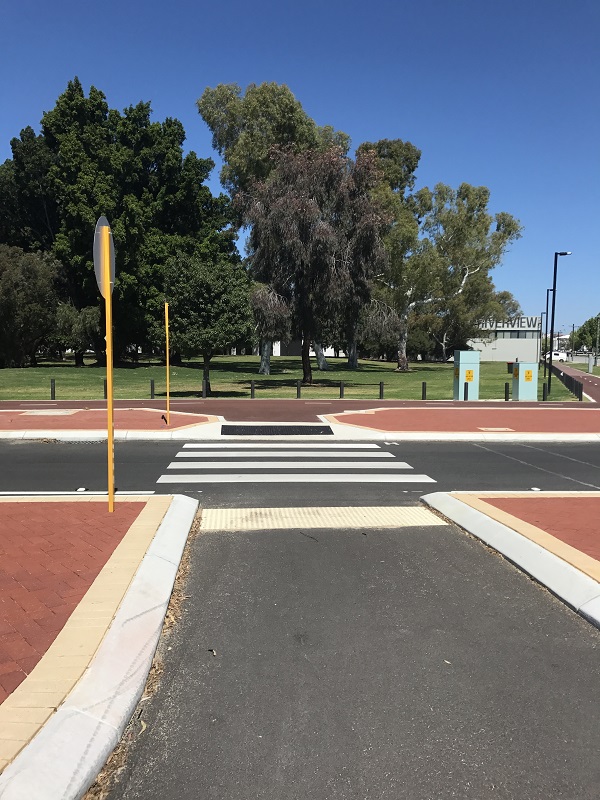 Unsignalised pedestrian crossing with lane narrowing in Australia. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Unsignalised pedestrian crossing with lane narrowing in Australia. Image credit: Alina Burlacu Urban road at a multimodal transport hub with sidewalks, bicycle lanes, median and pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Tianjin Urban Construction Design Institute
Urban road at a multimodal transport hub with sidewalks, bicycle lanes, median and pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Tianjin Urban Construction Design Institute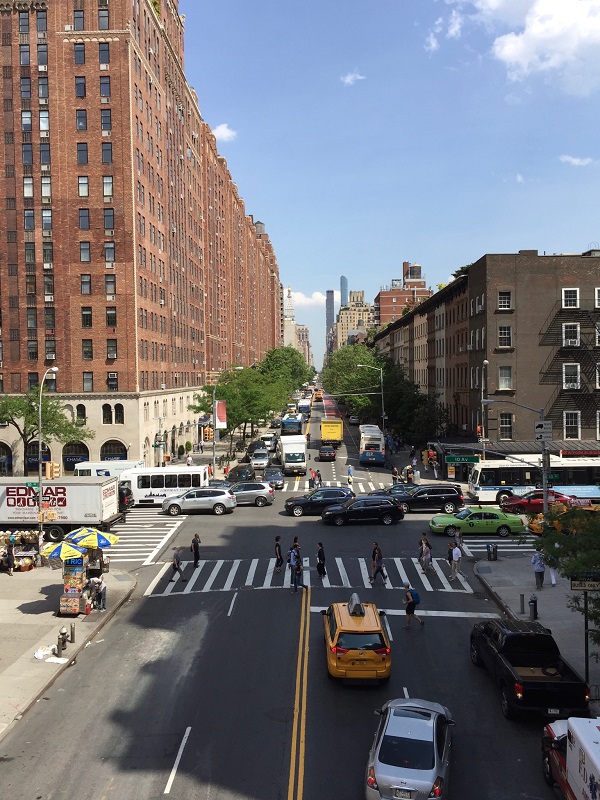 Urban street in New York, USA. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers
Urban street in New York, USA. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers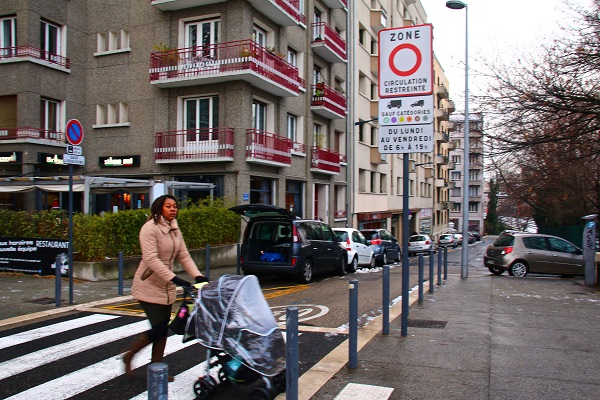 A mother crossing the road with a stroller. Photo credit: RdA Suisse
A mother crossing the road with a stroller. Photo credit: RdA Suisse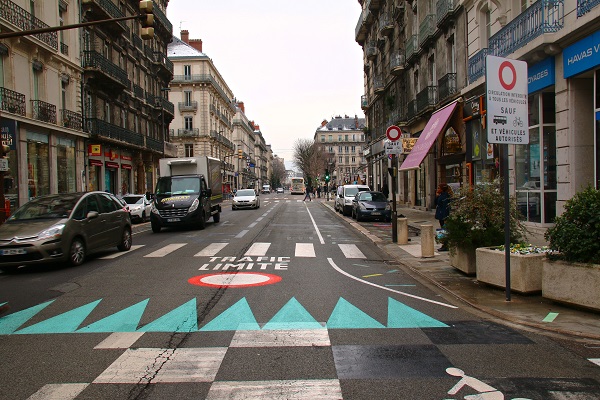 A slow speed pedestrian crossing. Photo credit: RdA Suisse.
A slow speed pedestrian crossing. Photo credit: RdA Suisse.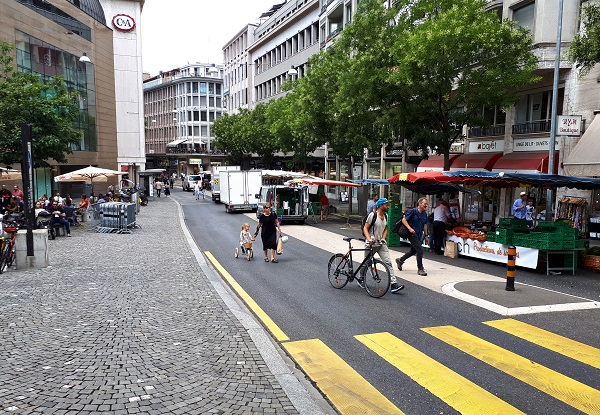 Pedestrians crossing a slow speed road. Photo credit: RdA Suisse
Pedestrians crossing a slow speed road. Photo credit: RdA Suisse Zebra crossing in Uzbekistan. Image credit: Anvar Matkarimov
Zebra crossing in Uzbekistan. Image credit: Anvar Matkarimov










