



Pedestrian Footpath
Increased safety for pedestrians. Improves facilities for pedestrians (improves accessibility). May help to increase walking as a mode of transport (environmental benefits and reduced traffic congestion). Walking can improve health and fitness.
Provision of footpaths should accord with the desired route of pedestrians with respect to important origins and destinations. Provision of footpaths should facilitate access to public transport facilities including bus stops and bus terminus. Where pedestrian volume is high, a reasonable Level of Service (LOS) of footpaths should be attained to encourage usage of the footpath. A routine maintenance programme is needed to ensure that footpaths are kept clean and level, free from defects and to prevent vegetation from causing an obstruction. Signage should be used to warn drivers of pedestrians if the road shoulder is commonly used as an informal footpath. Street traders, public utility apparatus and street furniture should not be allowed to obstruct the footpath. It is recommended that consideration be given to improving accessibility for the mobility impaired. This should include design features such as paved footpaths with sufficient width to accommodate wheelchairs, dropped kerbs at pedestrian crossing points, tactile paving and improved road markings and signs. Interruptions by obstructions and access openings should be minimised along footpaths. Accesses to parking areas and industrial facilities could be hazardous. The risk can be mitigated by ensuring adequate visibility and highlighting the conflict area in a different colour of the footpath surface.
Treatment Summary
40-60% |
Case Studies
Related Images

An obstructed footpath and pedestrian walking on the road. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers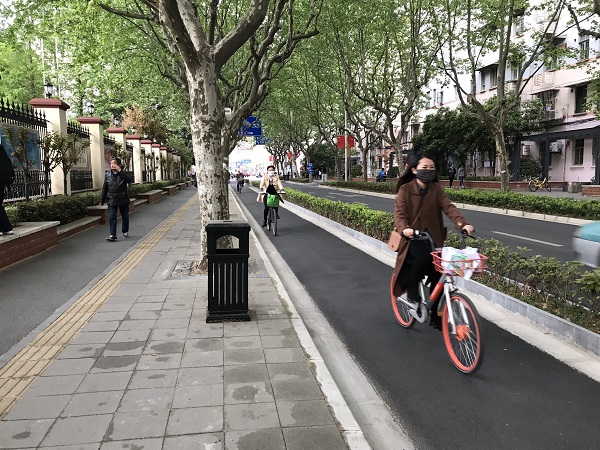 
Bicycle lane and sidewalk in China. Image credit: WRI 
Bicycle lane and sidewalk in Mexico. Image credit: Agustin Centeno 
Bollards protect a sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith 
Bollards to protect the sidewalk from vehicles in China. Image credit: Greg Smith 
Covered footpath in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu 
Covered footpath in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu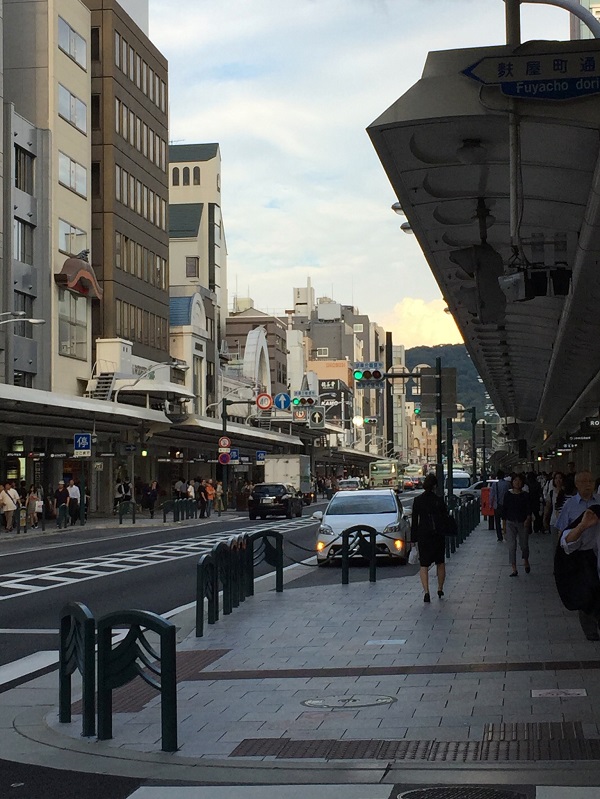 
Curb buildout to narrow pedestrian crossing width and creating parking space in Kyoto, Japan. Image credit: iRAP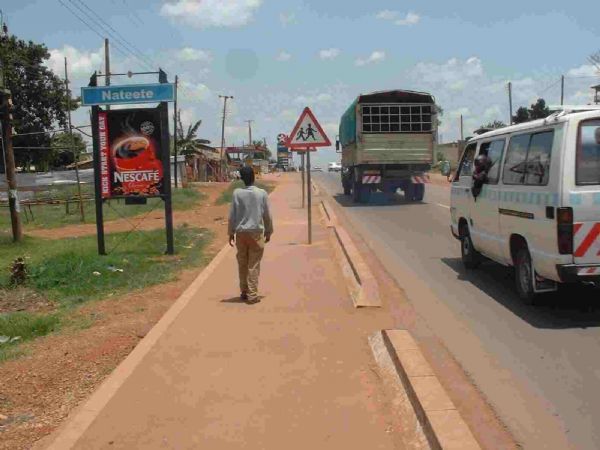 
A low-cost and easy to implement pedestrian footpath in Kampala, Uganda. Even simple footpaths like this one have the potential to significantly improve safety for pedestrians. Image credit: Allan Jones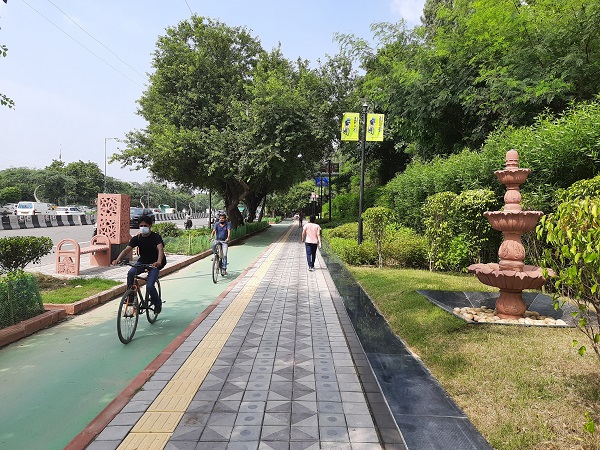 
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi India. Image credit: iRAP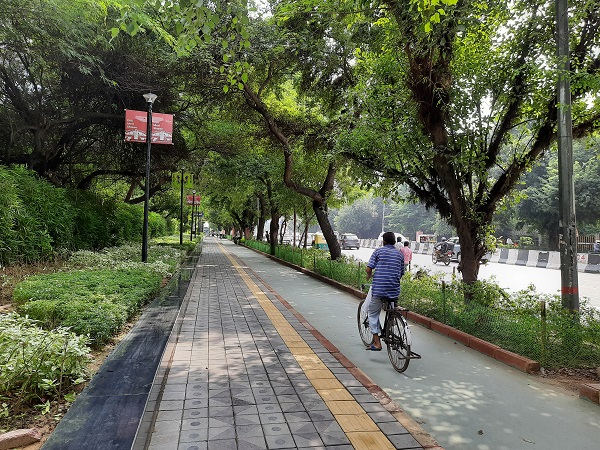 
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi India. Image credit: iRAP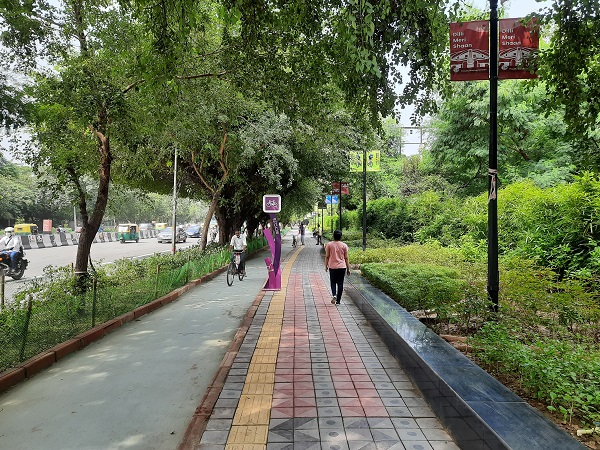 
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi, India. Image credit: iRAP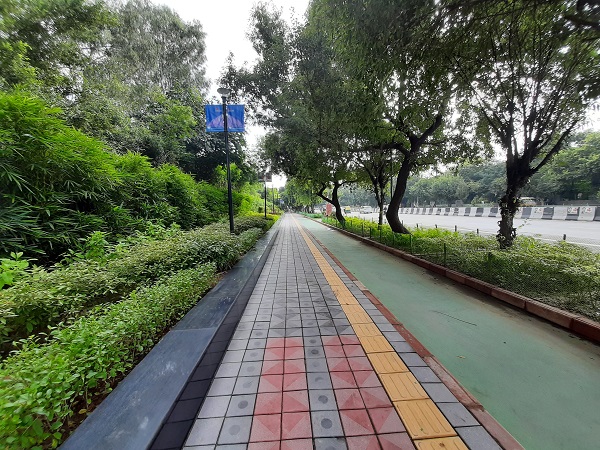 
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi India. Image credit: iRAP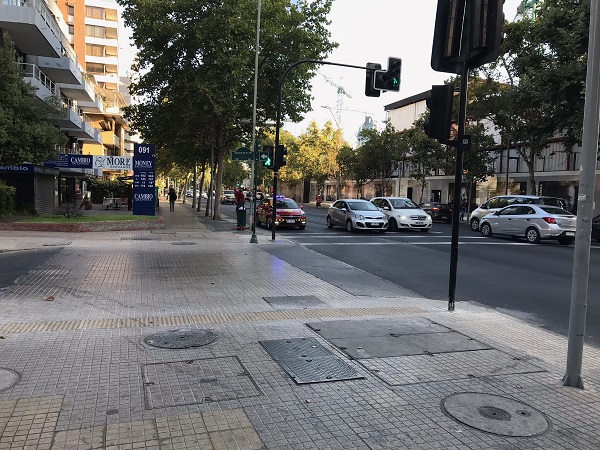 
Sidewalk. Image credit: iRAP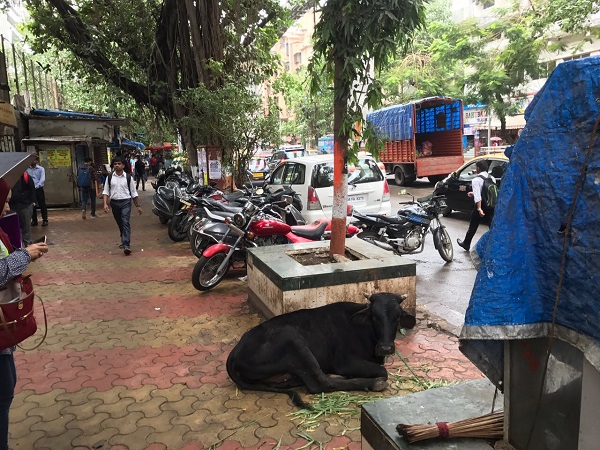 
Footpath in Mumbai. Image credit: Alina Burlacu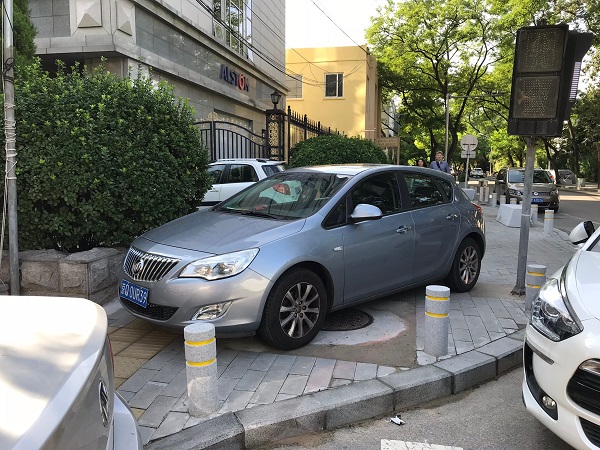 
Illegal parking on a footpath in Beijing, China. Image credit: iRAP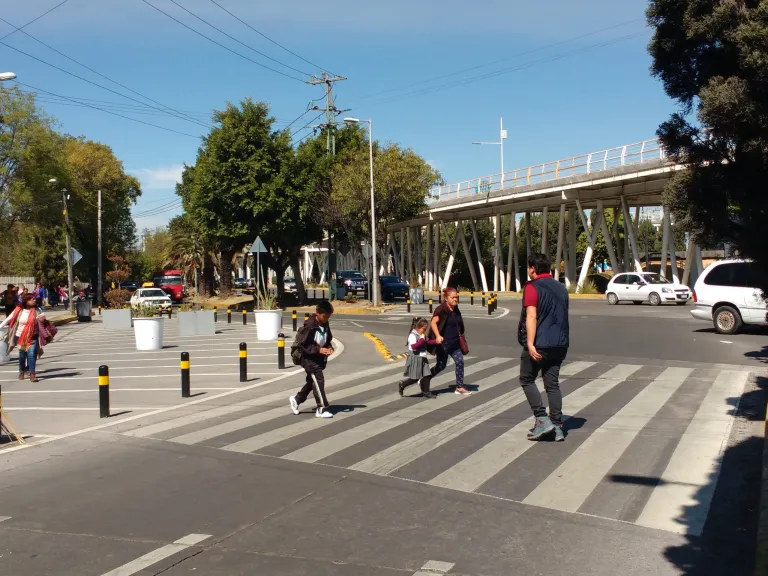 
Pedestrian crossing and sidewalk at a school in Mexico. Image credit: ITDP 
Informal footpath along a major road in India. Image Credit: IndiaRAP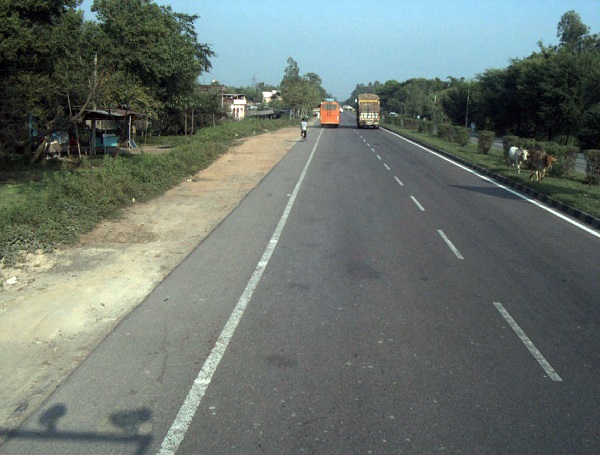 
Informal footpath along a National Highway in India. Image Credit: IndiaRAP 
Informal sidewalk in Uzbekistan. Image credit: Anvar Matkarimov 
3-leg intersection with pedestrian facilities. Image credit: Kerala State Transport Project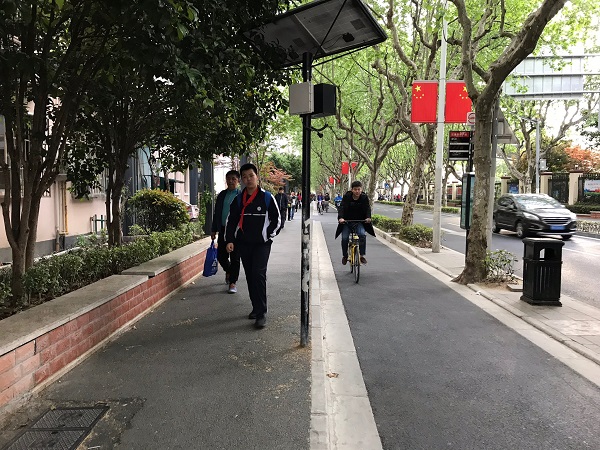 
Pedestrian and bicycle facilities in Shanghai. Image credit: Unknown 
Pedestrian crossing facility with footpath, wide centreline and speed transverse markings to calm speed on a state highway in Kerala, India. Image credit: Kerala State Transport Project 
Stop sign and sidewalk in United Arab Emirates. Image Credit: iRAP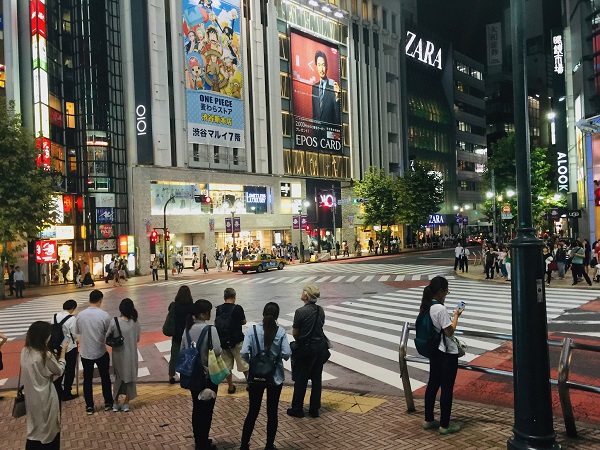 
Pedestrian crossing in Tokyo, Japan. Image Credit: iRAP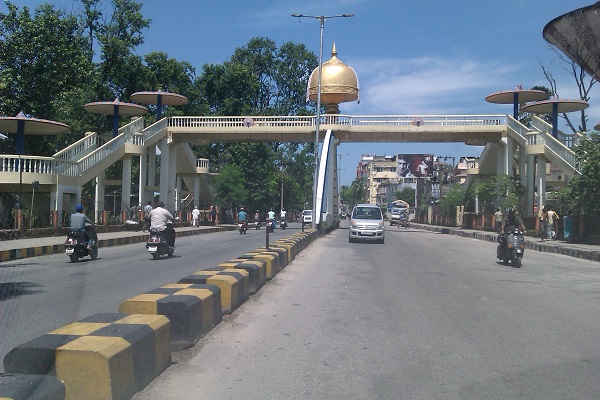 
Pedestrian footover bridge in India. Image credit: iRAP 
Pedestrians walking on informal footpath along a rural road in India. Image credit: iStock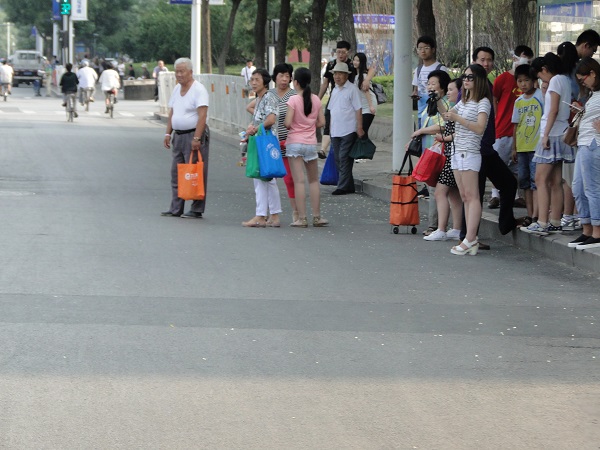 
Pedestrians spill onto the road from a sidewalk that does not have enough capacity in China. Image credit: Greg Smith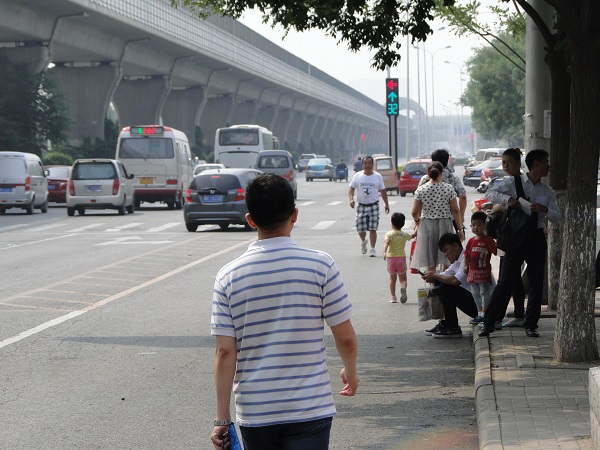 
Pedestrians walk on the road because of an obstructed sidewalk, China. Image credit: Greg Smith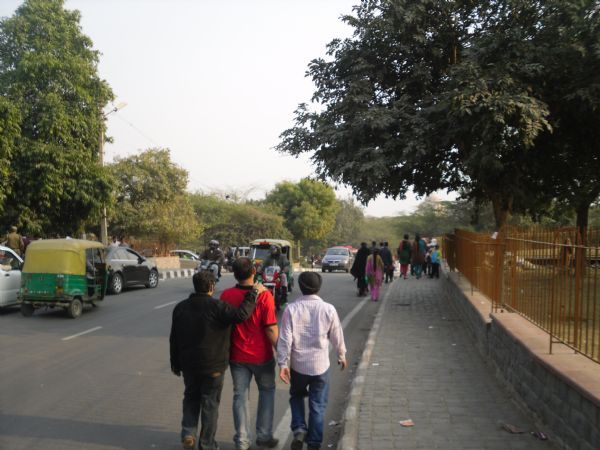 
Pedestrians walking in the road despite the presence of a footpath in New Delhi, India. Image credit: Greg Smith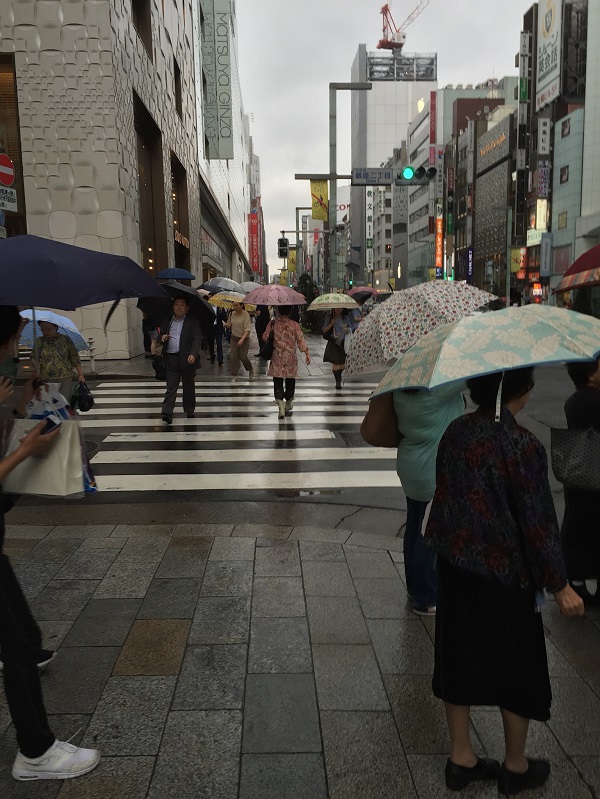 
Pedestrians in Tokyo, Japan. Image Credit: iRAP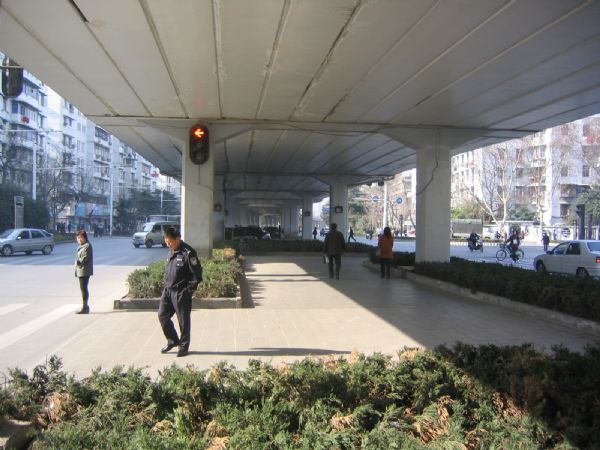 
Physical channelisation (and planting) under the flyover to provide a safe refuge for pedestrians to cross the road in two stages. Image credit: Gladys Frame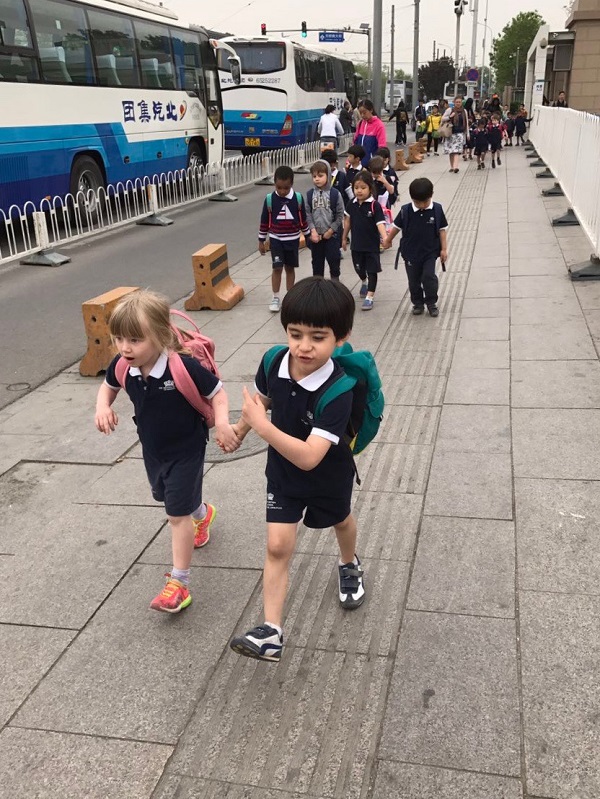 
Public transport in China (School children). Image credit: Monica Olyslagers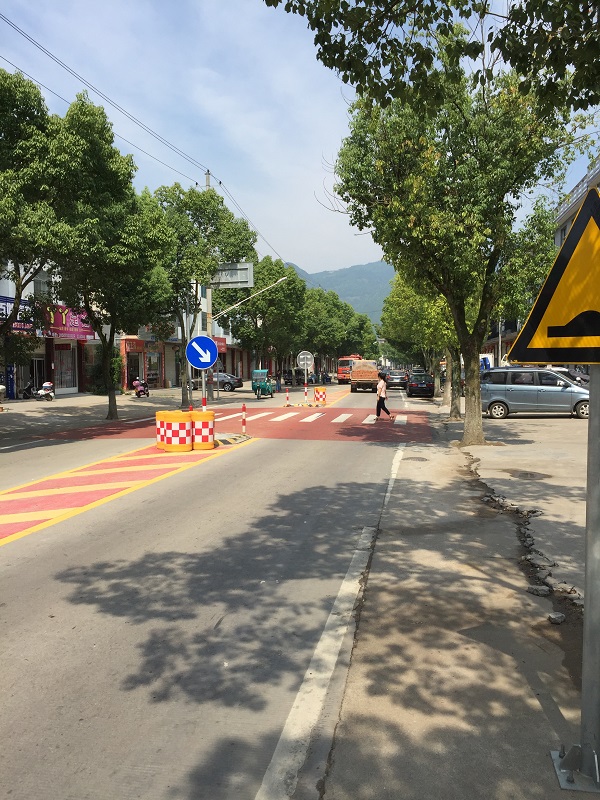 
Raised pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Greg Smith 
School safety improvements. Image credit: Asia Injury Prevention Foundation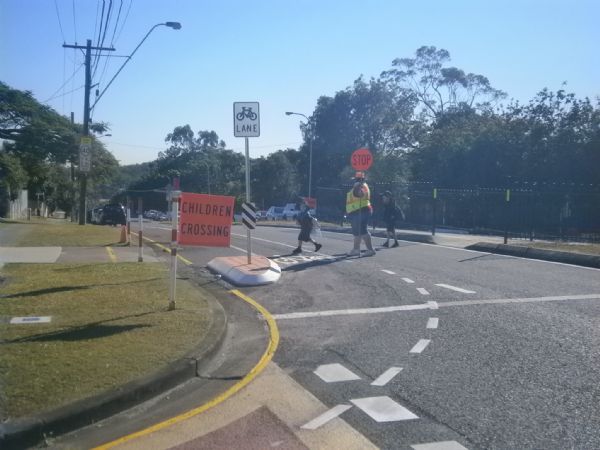 
School Zone crossing supervisor in Australia. Image credit: Unknown 
A sidewalk in China. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers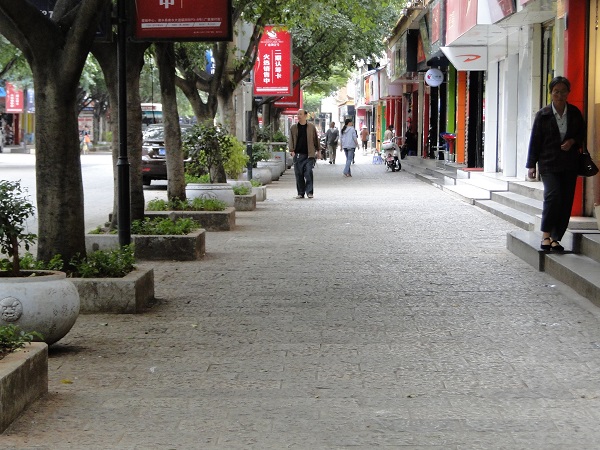 
A sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith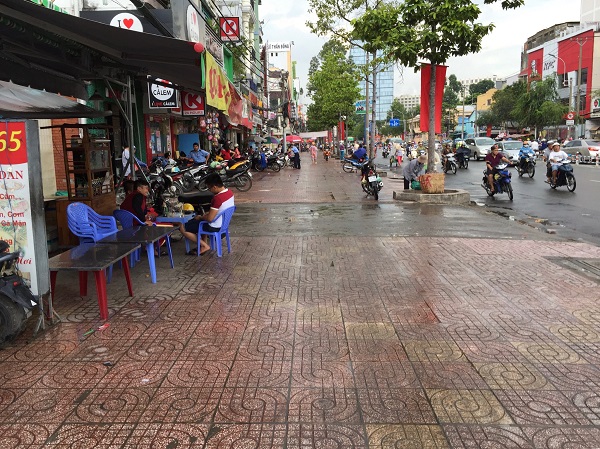 
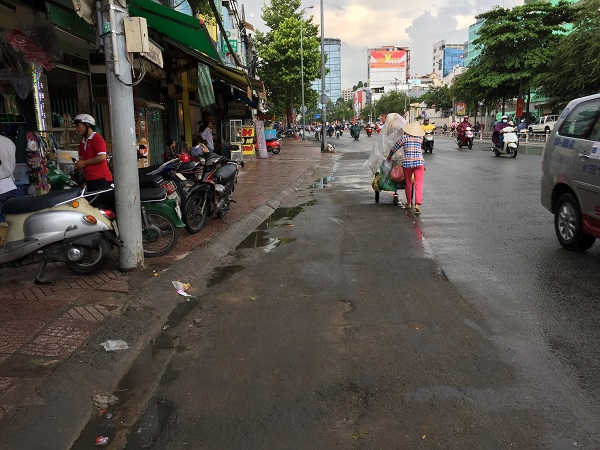
Sidewalk in Vietnam. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers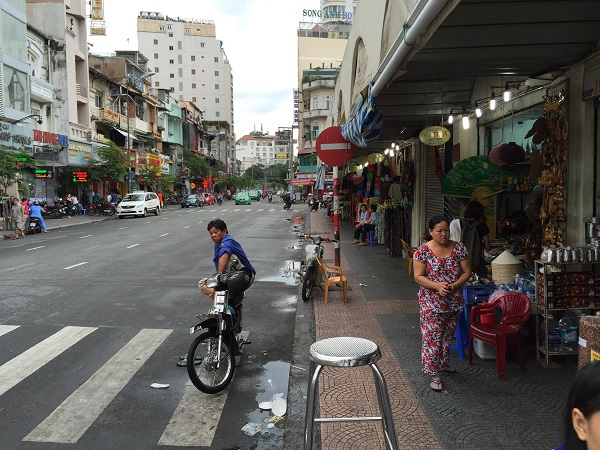 
Sidewalk in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers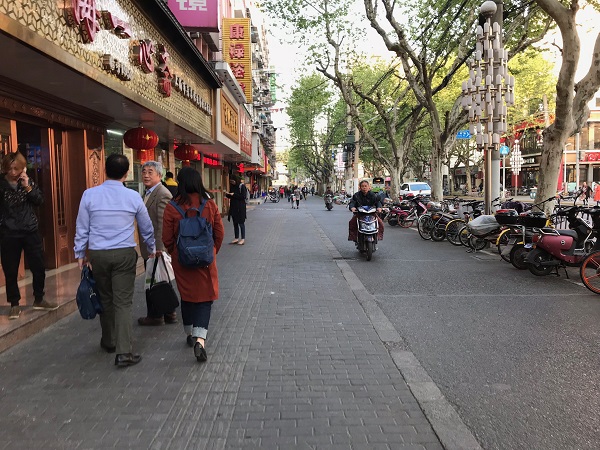 
A sidewalk in Shanghai, China. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers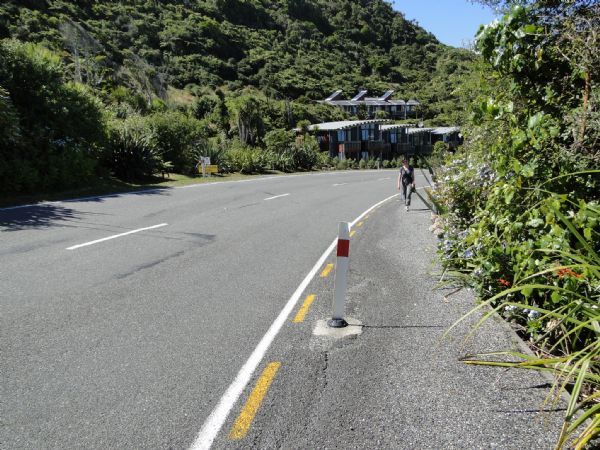 
Simple pedestrian footpath in a semi-urban area of New Zealand. Image credit: Greg Smith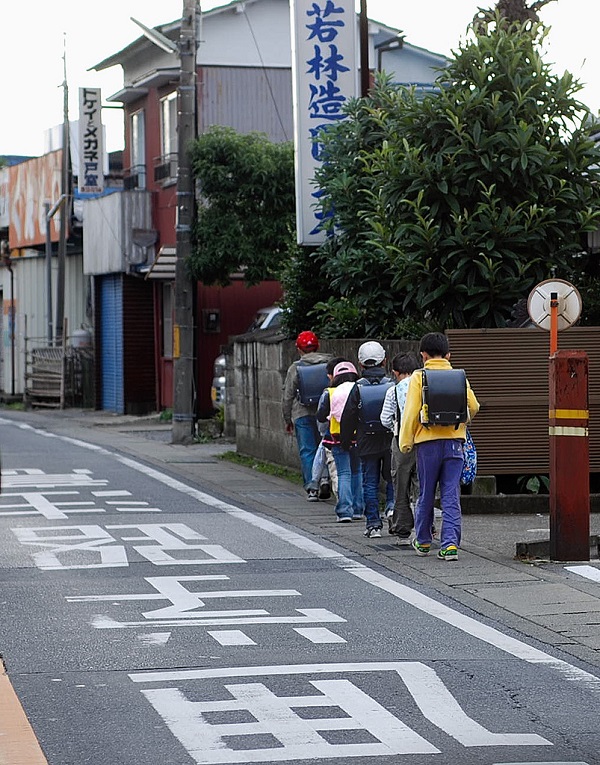 
Narrow sidewalk in Japan. Image credit: Michael Martin 
Street lights and sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith 
Low cost footpath in Uganda. Image credit: Allan Jones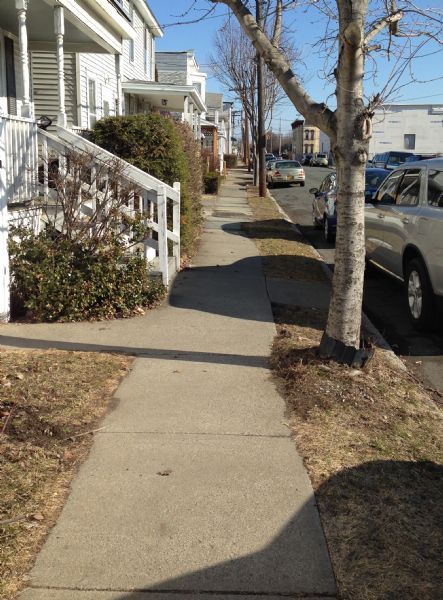 
Suburban sidewalk in the USA. Image credit: Unknown 
Urban road at a multimodal transport hub with sidewalks, bicycle lanes, median and pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Tianjin Urban Construction Design Institute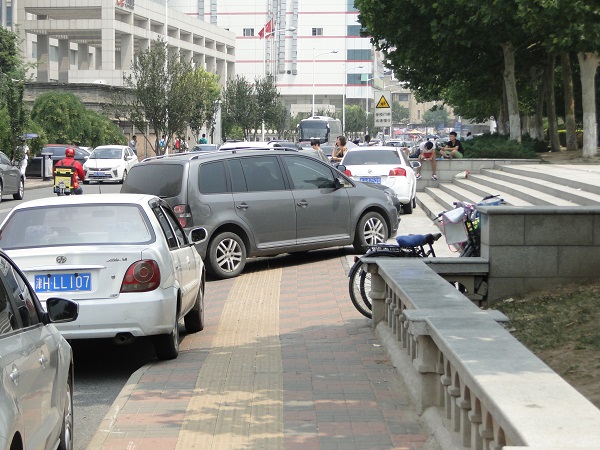 
Vehicles obstruct a sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith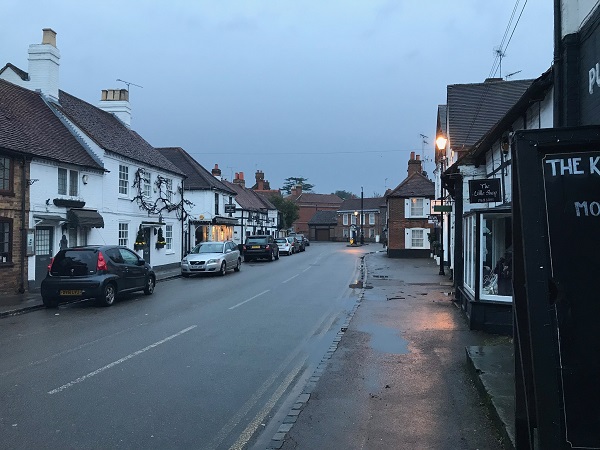 
Village street in England, UK. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers










