



Pedestrian Crossing - Grade Separation
Most pedestrian crashes occur while the pedestrian was attempting to cross the road. One way of preventing crashes between vehicles and pedestrians is placing them at different levels, or ‘grade separating’ them.
In urban situations where pedestrian crossing signals would cause congestion or crashes (due to high traffic speeds), a grade separated pedestrian crossing, such as an overpass (or bridge, footover bridge) or an underpass, may be used. Outside of urban areas in situations where there is pedestrian demand in high-speed environments, this treatment may also be applied.
Grade separated pedestrian crossings reduce pedestrian crashes but they also have some disadvantages:
- they are costly
- they sometimes become crowded with street traders
- pedestrians may avoid them if there are a lot of steps to climb up or down
- if they are not well-lit and patrolled, they may pose a personal security risk
- underpasses are susceptible to flooding and can become unusable if not routinely maintained.
- Reduced pedestrian/vehicular conflict.
- Can help to reduce fatal and serious injuries involving pedestrians and bicyclists.
- Traffic flow improvements.
- Grade-separated pedestrian crossings are more attractive if detour and level difference are reduced by taking advantage of local topography and vertical profile of a road.
- Semi-depressed underpasses can be attractive for pedestrians and non-motorised users.
- Pedestrians tend only to use crossing facilities located at, or very near, to where they want to cross the road. Pedestrian fencing can be used to encourage pedestrians to use crossing facilities.
- Where a lot of bicyclist traffic is present a pedestrian underpass or overpass can be used by cyclists as well as pedestrians, but this will require shallow approach ramps and therefore additional land.
- Consideration should be given to improving accessibility for the mobility impaired. This may include design features such as sufficient width to accommodate wheelchairs and ramps or lifts as an alternative to steps.
The Star Rating Demonstrator is a freely available tool with the iRAP online software, ViDA. With the Star Rating Demonstrator, it is possible to explore the impact that this Safer Roads Treatment has on risk.
Treatment Summary
Costs | High |
Treatment life | 20 years + |
Potential casualty reduction | 60% or more |
Case Studies
Related Images
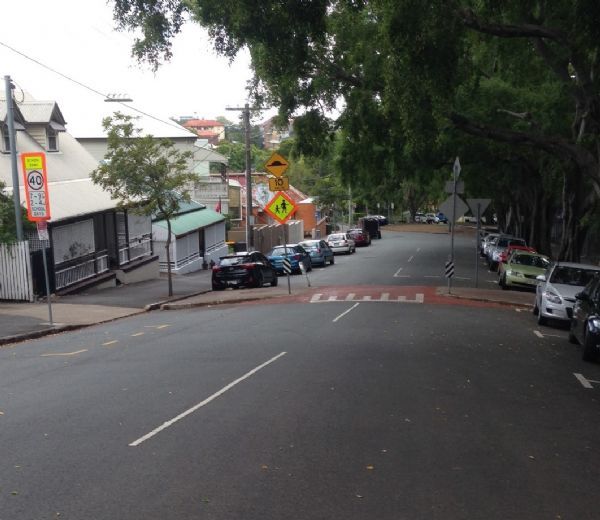 A raised pedestrian crossing with kerb build-out in a school zone in Brisbane, Australia. This is an effective traffic calming measure whilst providing a safe place to cross. Image credit: Luke Rogers
A raised pedestrian crossing with kerb build-out in a school zone in Brisbane, Australia. This is an effective traffic calming measure whilst providing a safe place to cross. Image credit: Luke Rogers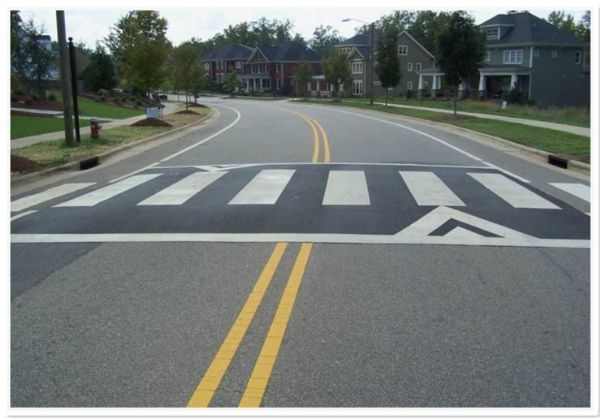 A raised pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Unknown
A raised pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Unknown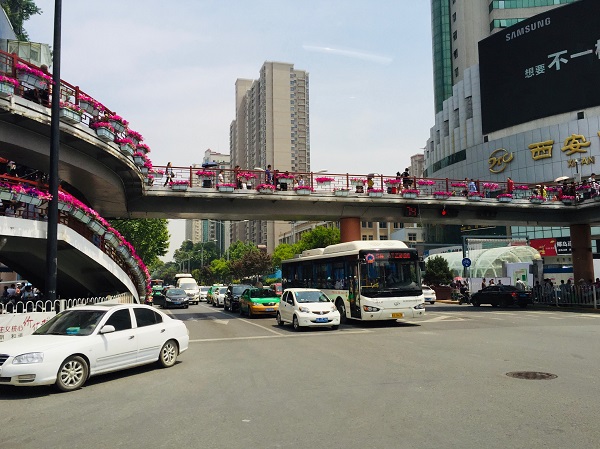 Pedestrian bridge. Image credit: iRAP
Pedestrian bridge. Image credit: iRAP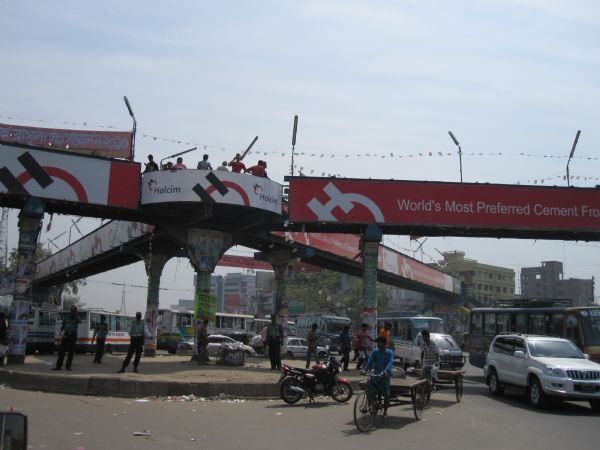 Grade separated pedestrian crossing in Bangladesh. Image credit: Richard Wix, ARRB
Grade separated pedestrian crossing in Bangladesh. Image credit: Richard Wix, ARRB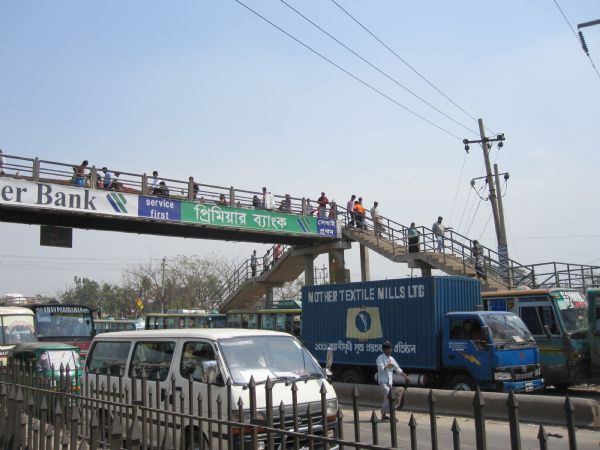 Grade separated pedestrian crossing in Bangladesh. Image credit: Richard Wix, ARRB
Grade separated pedestrian crossing in Bangladesh. Image credit: Richard Wix, ARRB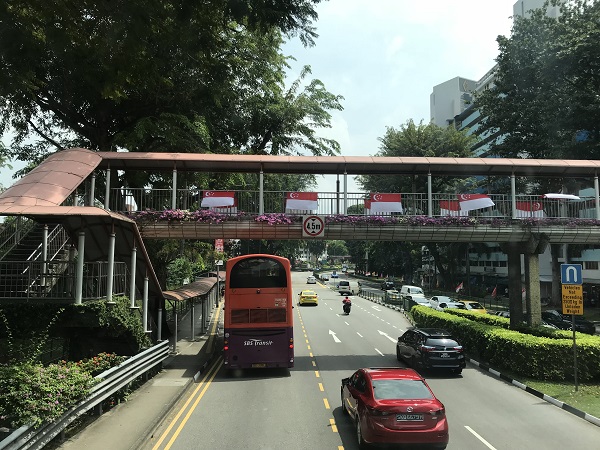 Grade separated pedestrian crossing in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Grade separated pedestrian crossing in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu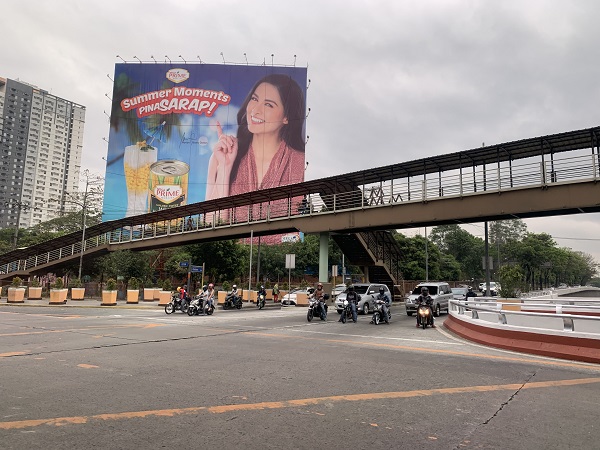 Long pedestrian bridge with limited access in the Philippines. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Long pedestrian bridge with limited access in the Philippines. Image credit: Alina Burlacu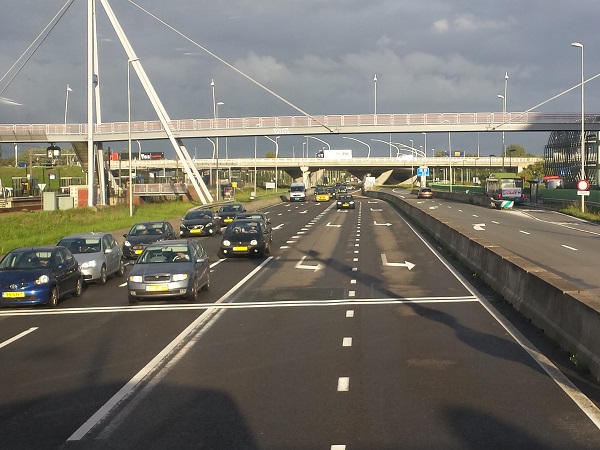 Pedestrian bridge in the Netherlands. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Pedestrian bridge in the Netherlands. Image credit: Alina Burlacu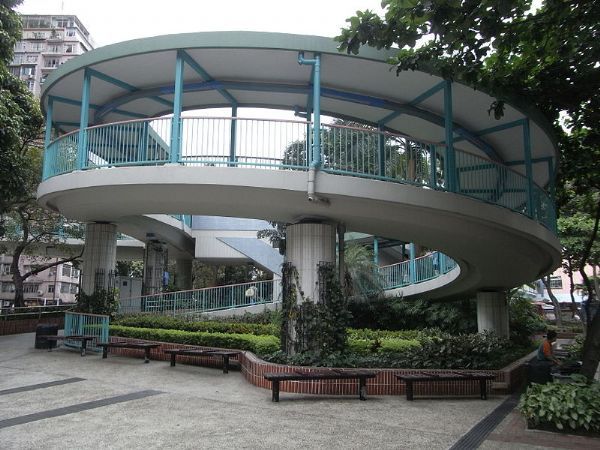 Pedestrian bridge with spiral ramp Hong Kong. Image credit: Wyuekmom, Wikimedia
Pedestrian bridge with spiral ramp Hong Kong. Image credit: Wyuekmom, Wikimedia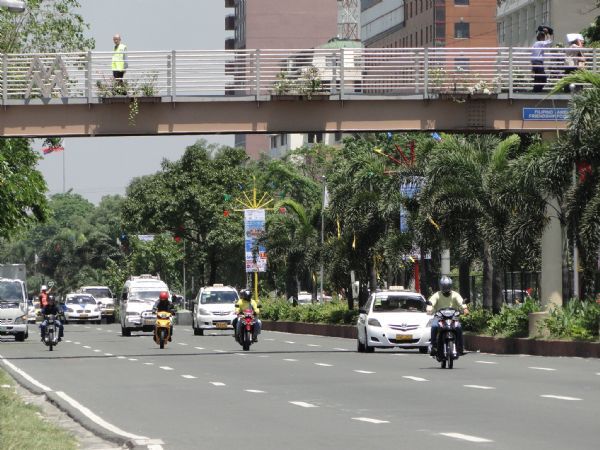 Pedestrian footbridge - Roxas Blvd Manila, Philippines. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrian footbridge - Roxas Blvd Manila, Philippines. Image credit: Greg Smith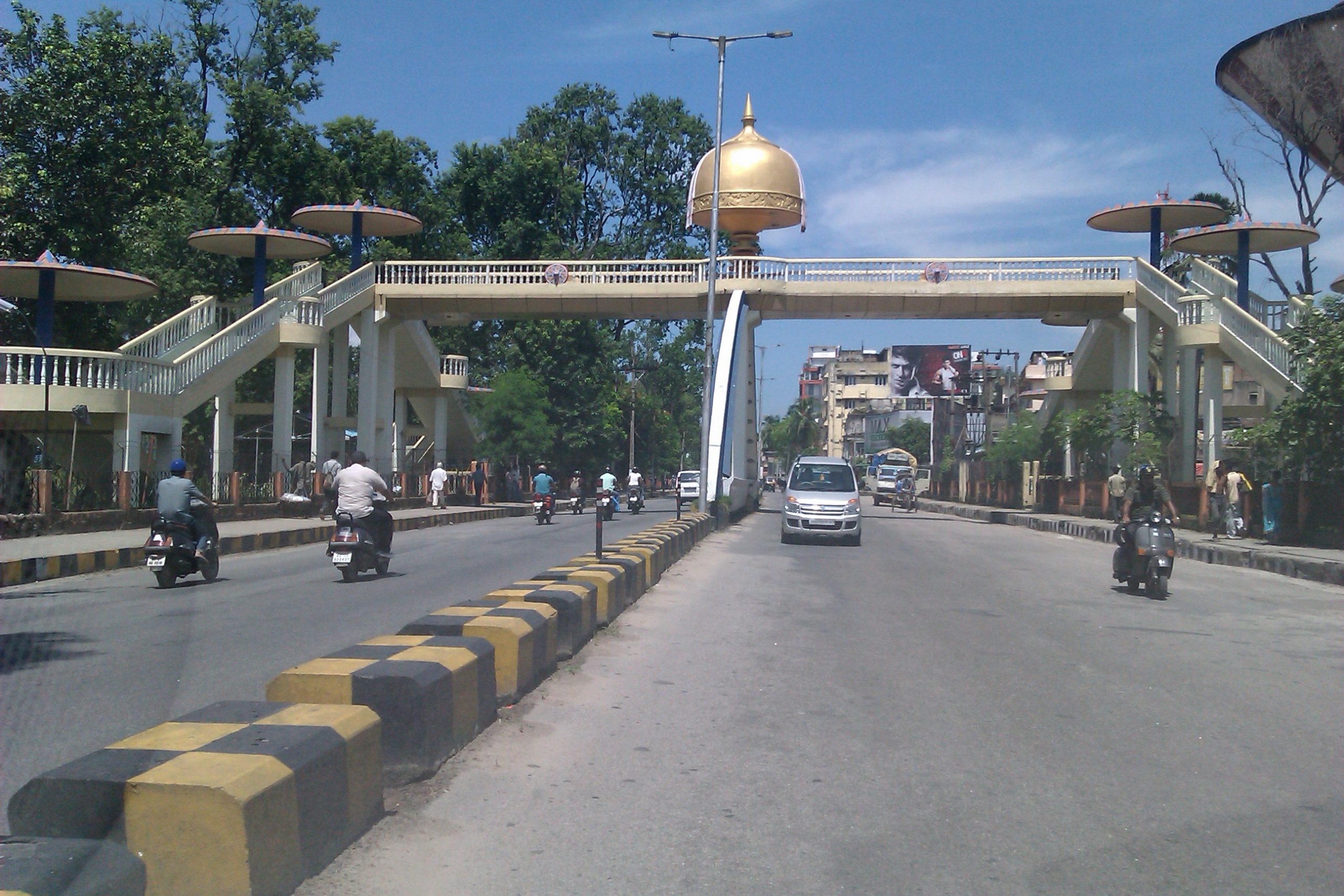 Pedestrian footover bridge in India. Image credit: iRAP
Pedestrian footover bridge in India. Image credit: iRAP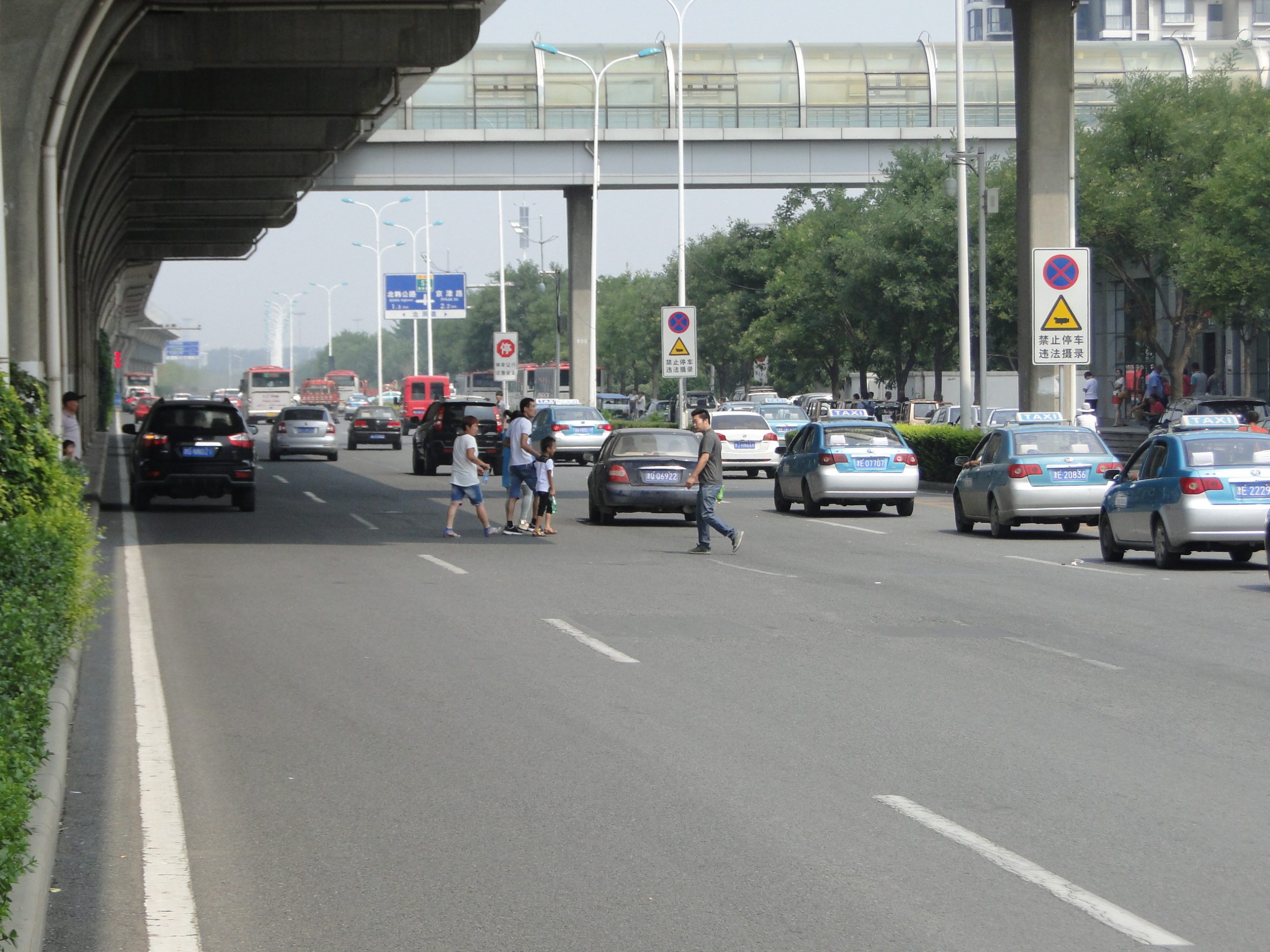 Pedestrians cross busy multilane road underneath a pedestrian bridge in China. Image Credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians cross busy multilane road underneath a pedestrian bridge in China. Image Credit: Greg Smith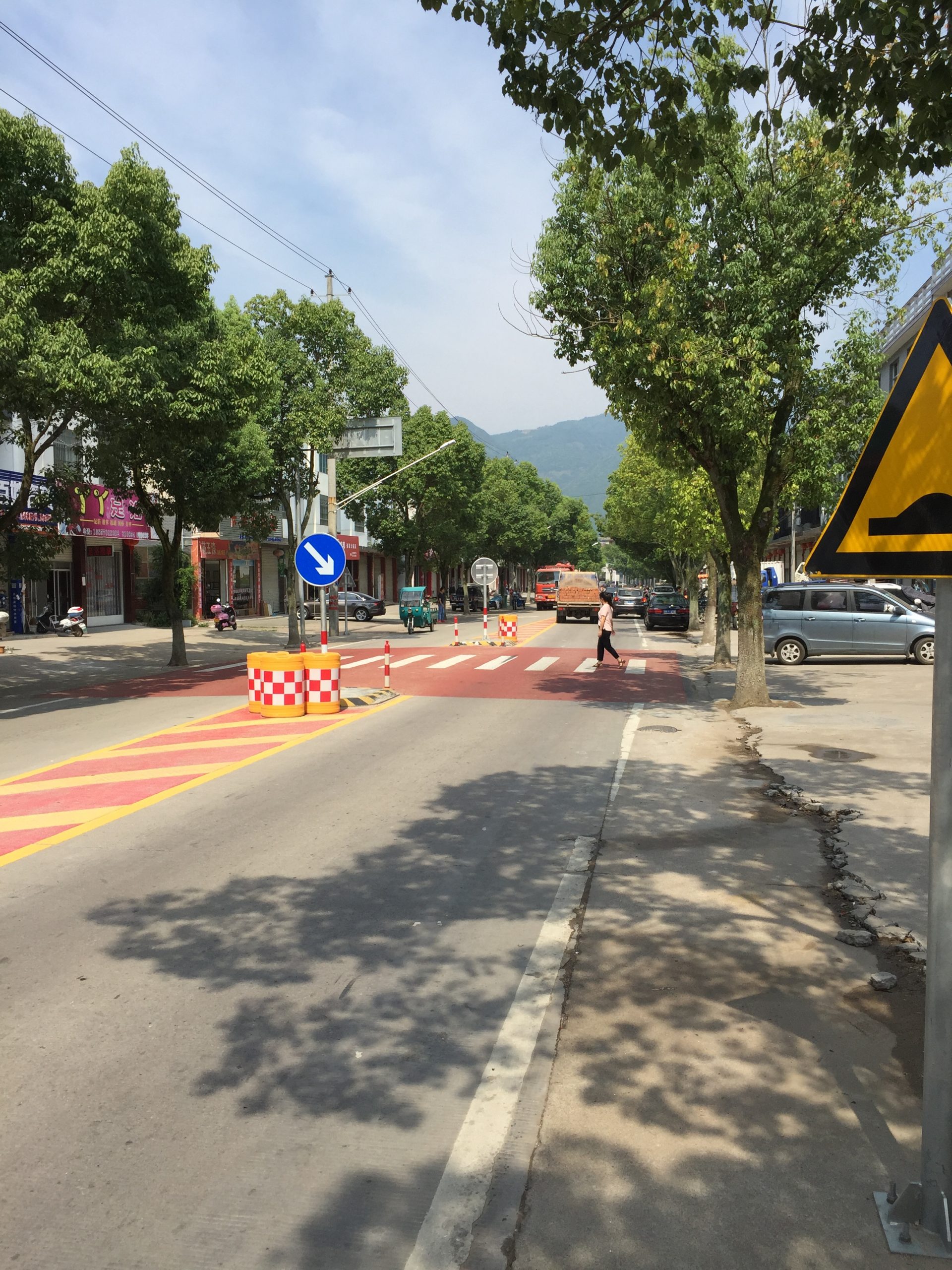 Raised pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Greg Smith
Raised pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Greg Smith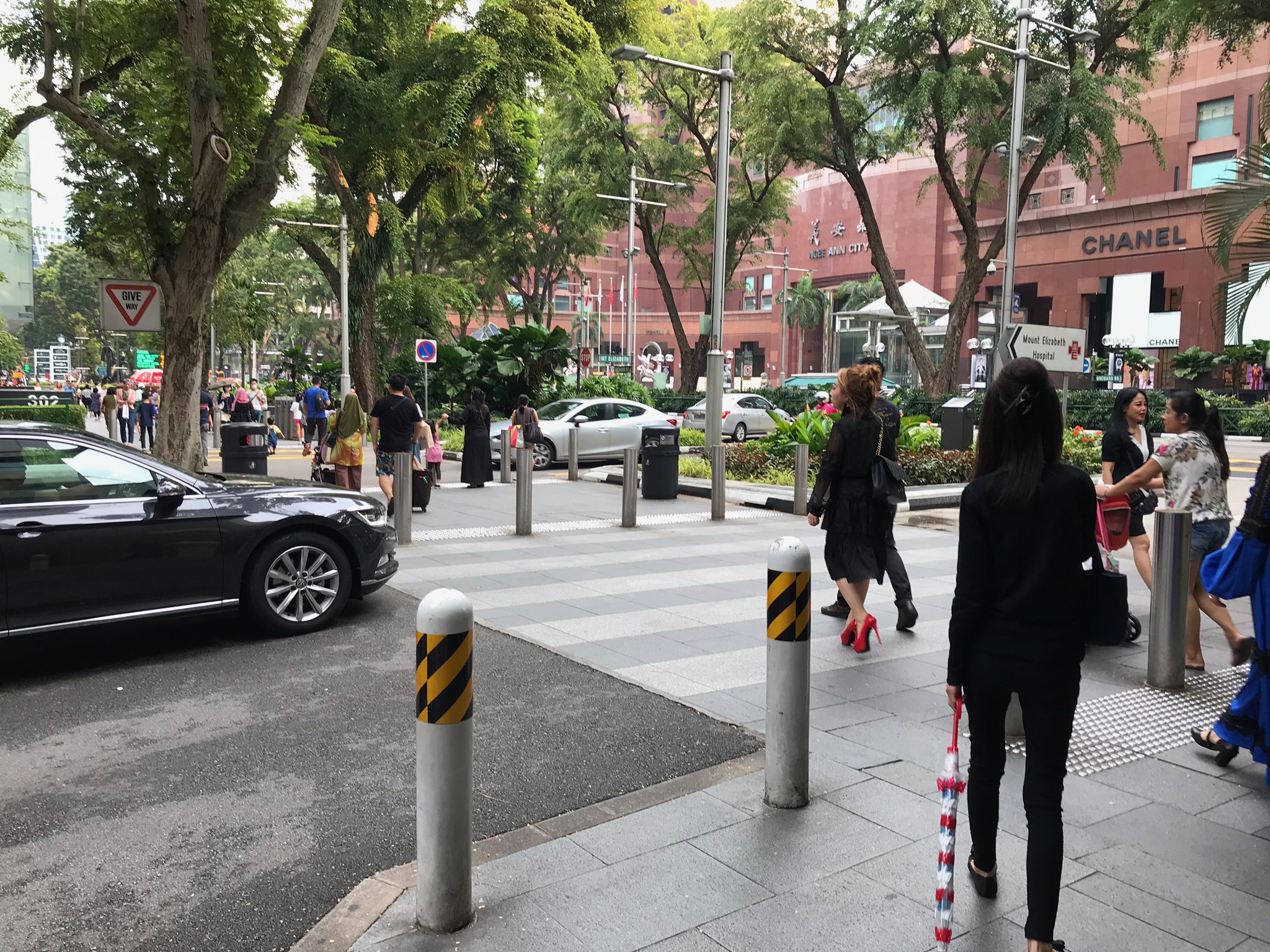 Raised pedestrian crossing facility in China. Image credit: Unknown
Raised pedestrian crossing facility in China. Image credit: Unknown










