



Lane Change
- Inappropriate speeds.
- Poor pavement skid resistance.
Unexpected or poor lane drop-offs or merge areas. Inadequate length for merging or weaving. Roadside activity .- Poor directional signs or lane markings.
Poor visibility including ‘blind spots’ and at merging areas and towards diverging areas. - Driver/rider fatigue.
- Alcohol/drugs/medication impairment.
Distraction, including inattention due to mobile phone use. Information overload (too many driving decisions to be made at once). Lack of familiarity with the route. Lack of vehicle safety devices .- Poor condition of vehicle tyres, lights, and brakes.
Case Studies
| 10 – 25% | ||
| 10 – 25% | ||
| 10 – 25% | ||
| 25 – 40% | ||
| 10 – 25% | ||
| 10 – 25% | ||
| 25 – 40% | ||
| 10 – 25% | ||
| 10 – 25% | ||
| 25 – 40% | ||
| 25 – 40% |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – | |
| – | – |
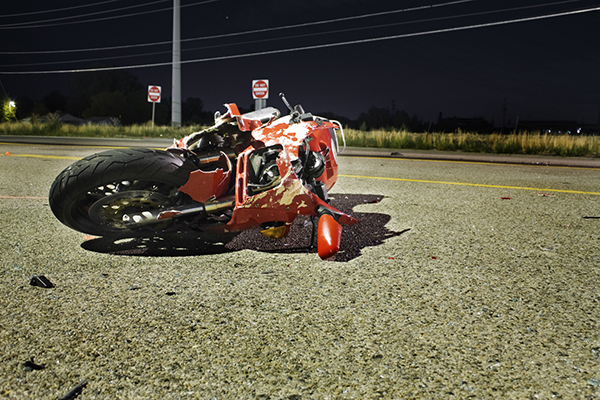

A motorcycle crash. Image credit: iStock 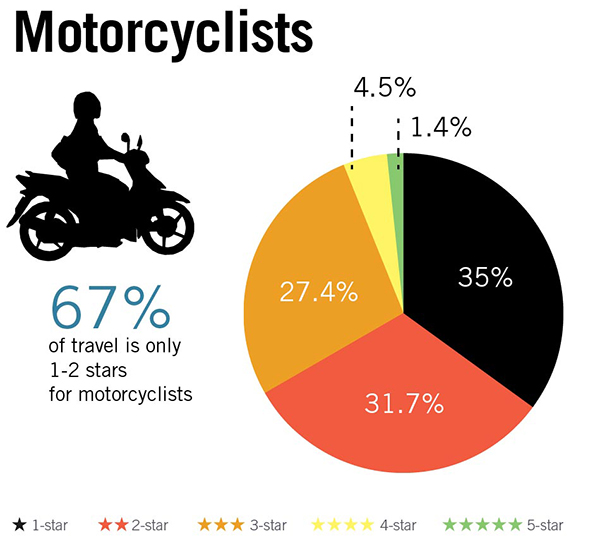
Motorcyclist Star Ratings by road user type based on a 358,000km sample of roads across 54 countries. Image credit: iRAP 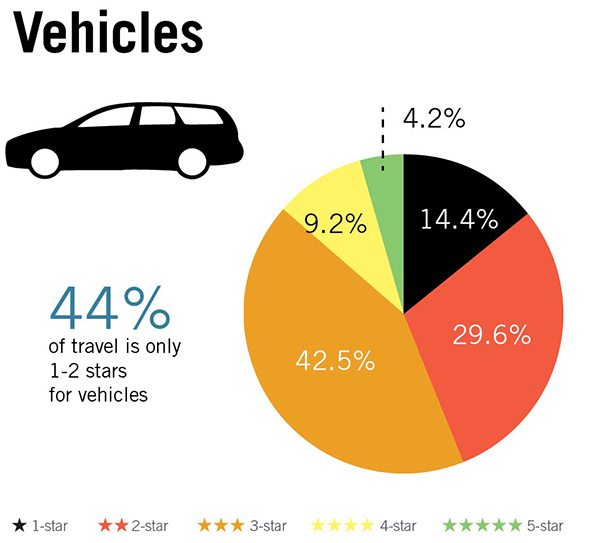
Vehicle occupant Star Ratings by road user type based on a 358,000km sample of roads across 54 countries. Image credit: iRAP 
Lane change left 
Side swipe crash in Singapore. Image credit: Alina Burlacu








