



Intersection
Intersection crashes are one of the most common types of crash problem, particularly in urban areas. In rural areas, or where vehicle speeds are high, the consequence of collisions at intersections can be particularly severe.
The chances of avoiding serious injury or death reduce dramatically above 50 km/h for side impacts for the most modern types of cars, and is far less than this for older vehicles, and particularly for vulnerable road users.
A number of different intersection crash types can occur, including:
- Collisions with pedestrians and bicyclists.
- Collision between oncoming vehicles and motorcycles, particularly when one is turning across traffic.
- Right-angle collisions, where neither vehicle or motorcycle is turning (often occurring at high speed).
- Right-angle or side-swipe collisions where one or more vehicles or motorcycles are turning.
- Rear-end crashes.
Typical factors which may add to intersection crash risk include:
- Inappropriate speeds.
- Lack of footpaths, pedestrian crossings or bicycle facilities.
- Lack of treatment such as delineation or roundabout.
- Inadequate sight distance to on-coming vehicles.
- Lack of intersection visibility including a lack of street lighting (road users are not aware of the intersection).
- Poor pavement skid resistance.
- Lack of gaps in traffic.
- Driver/rider fatigue.
- Alcohol/drugs/medication impairment.
- Distraction, including inattention due to mobile phone use.
- Overtaking errors, including poor judgement of the approaching vehicle speed.
- Lack of vehicle safety devices.
- Poor condition of vehicle tyres, lights, brakes and brake lights.
Case Studies
| Examples of related Case Studies |
|---|
| Saving lives with car seats in the Philippines |
| RAP Partnerships Saving Lives: Great Britain |
| A404 Amersham |
| Intersection speed zones |
| Rural roundabouts |
Safer Roads
Safer Vehicles
Safer People
Safer Roads
| Name | Cost rating | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Delineation | Low | 10 – 25% |
| Intersection – Delineation | Low | 10 – 25% |
| Intersection – Grade Separation | High | 25 – 40% |
| Intersection – Roundabout | Low to Medium | 60% or more |
| Intersection – Signalise | Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Intersection – Turn Lanes (Signalised) | Low to Medium | 10 – 25% |
| Intersection – Turn Lanes (Unsignalised) | Low to Medium | 10 – 25% |
| One Way Network | Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Parking Improvements | Low to Medium | 10 – 25% |
| Railway Crossing | Medium | 60% or more |
| Skid Resistance | Low to Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Speed Management | Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Traffic Calming | Medium to High | 25 – 40% |
Safer Vehicles
| Name | Cost rating | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Vehicle Standards | – | – |
| New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) | – | – |
| Used Car Safety Ratings | – | – |
| Safety Features and Devices | – | – |
| Vehicle Roadworthiness | – | – |
Safer People
| Name | Cost rating | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Addressing Alcohol and Other Drugs | – | – |
| Child Safety Initiatives | – | – |
| Education | – | – |
| Enforcement | – | – |
| Fatigue Management | – | – |
| Helmets and Protective Clothing | – | – |
| Licensing | – | – |
| Publicity | – | – |
| Safe Speed | – | – |
| Seatbelts | – | – |
Related Images
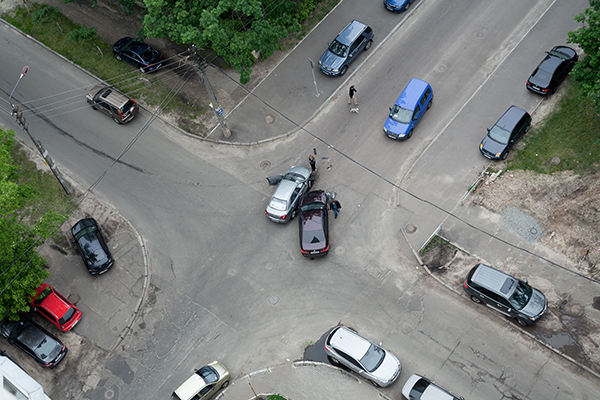 An intersection crash between two cars Image credit: iStock
An intersection crash between two cars Image credit: iStock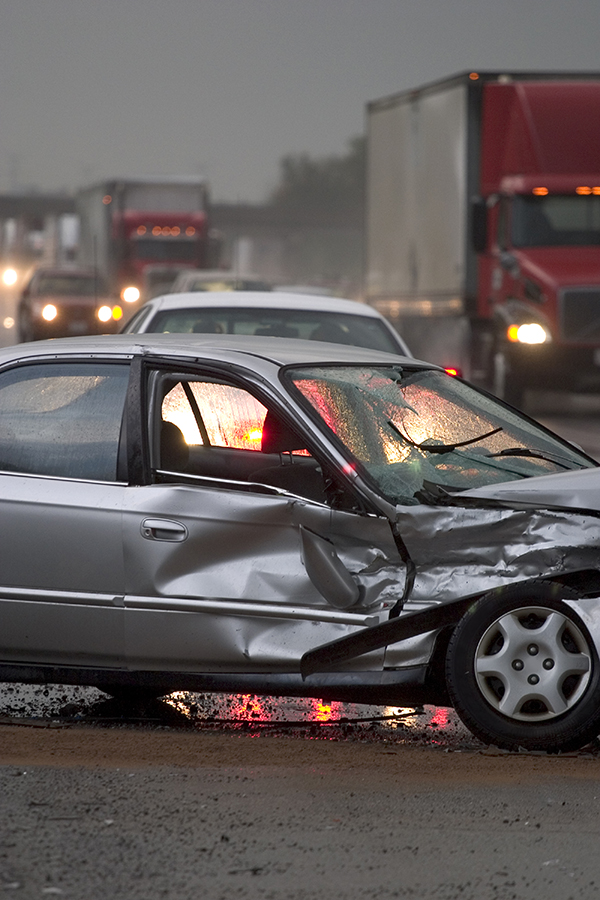 An intersection crash. Image credit: iStock
An intersection crash. Image credit: iStock A 4-leg intersection with poor delineation. Image credit: AusRAP
A 4-leg intersection with poor delineation. Image credit: AusRAP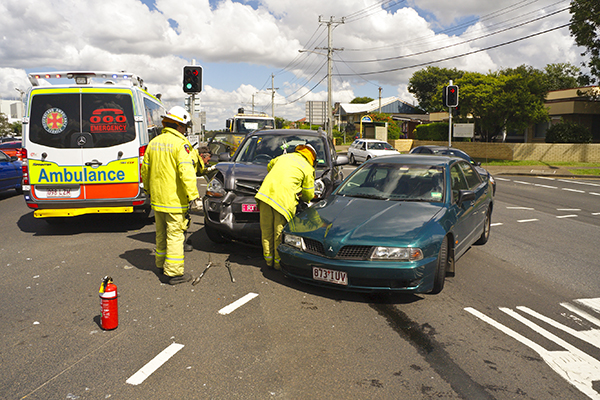 Emergency response to a crash between two cars at an intersection. Image credit: iStock
Emergency response to a crash between two cars at an intersection. Image credit: iStock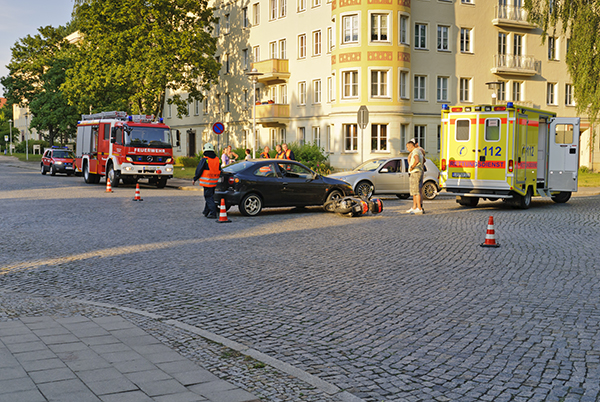 Emergency response to an intersection crash involving a car and a moped. Image credit: iStock
Emergency response to an intersection crash involving a car and a moped. Image credit: iStock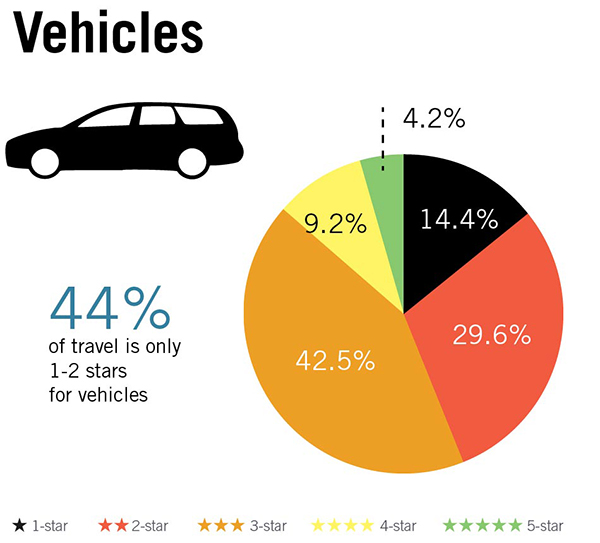 Vehicle occupant Star Ratings by road user type based on a 358,000km sample of roads across 54 countries. Image credit: iRAP
Vehicle occupant Star Ratings by road user type based on a 358,000km sample of roads across 54 countries. Image credit: iRAP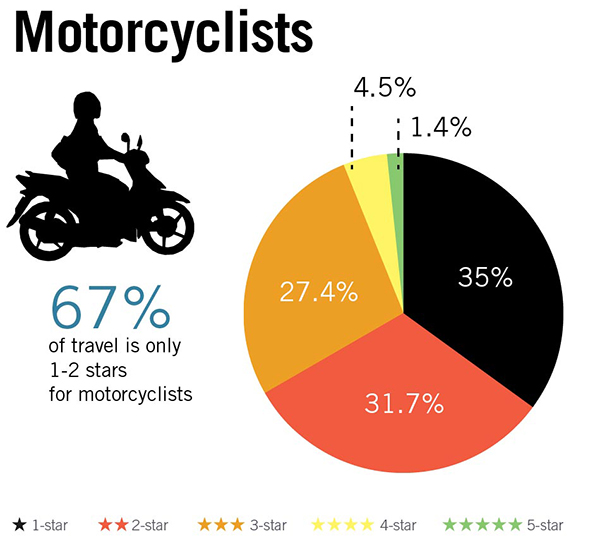 Motorcyclist Star Ratings by road user type based on a 358,000km sample of roads across 54 countries. Image credit: iRAP
Motorcyclist Star Ratings by road user type based on a 358,000km sample of roads across 54 countries. Image credit: iRAP








