



Duplication
Road duplication or ‘dualling’ involves changing a single carriageway road to a dual carriageway road by building a second separate carriageway, usually alongside the first.
Road duplication provides a safety benefit through provision of a central median barrier or strip of land (median or central reservation), thereby reducing the chances of head-on crashes.
Divided roads range from high speed, access-controlled roads to moderate speed arterial roads with at-grade intersections. In between, divided roads may consist of a mix of grade-separated and at-grade intersections.
This is costly and requires a large amount of space. Because it is so costly, road duplication projects are often carried out in a staged fashion, in order to make use of limited road funds. Duplication is typically only economically viable at higher traffic flow levels.
- Separation of the opposing traffic flows, and therefore reduced head-on crashes.
- Simpler traffic movements leading to less opportunity for conflict.
- Redirection of turning movements to safer locations.
- Protection for turning traffic.
- Reduced traffic congestion.
- This treatment is costly, and other lower cost treatments (such as median barrier installation) should also be considered.
- Requires a large amount of land.
- Community acceptance of the medians that restrict turning movements or restrict pedestrian movements may be an issue.
- Selection of the type of divided road should accord with the traffic function. Speed limits should be self-explaining to drivers in terms of road alignment, cross-sections and road furniture.
- Since divided roads are prone to speeding during light traffc, intersections, accesses, pedestrian crossings, U-turning facilities etc. need to be designed with great caution.
- At-grade intersections i.e. priority control, signalized control and roundabouts on divided roads should be planned with great caution due to potential high speeds and increased conflict points.
- U-turning may be provided at roundabouts or grade-separated intersections. Direct U-turning with median openings needs to be carefully planned.
- At the end of a divided road, strong treatment is necessary to reduce speed progressively and to assist drivers in adapting to the change in road condition.
The Star Rating Demonstrator is a freely available tool with the iRAP online software, ViDA. With the Star Rating Demonstrator, it is possible to explore the impact that this Safer Roads Treatment has on risk.
Treatment Summary
Costs | High |
Treatment life | 20 years + |
Potential casualty reduction | 25-40% |
Case Studies
| Examples of related Case Studies |
|---|
| El Salvador’s Coastal Highway |
| Road Safety – Catalogue Of Case Studies |
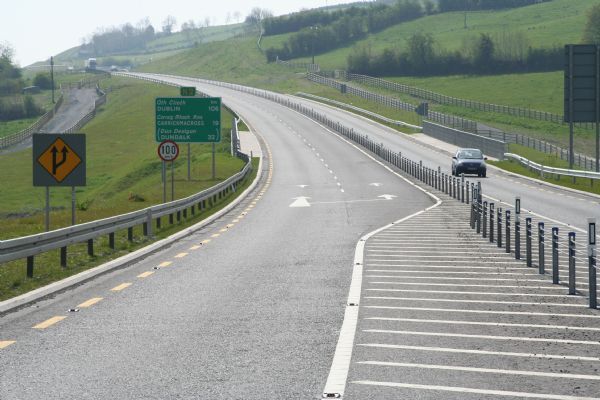 A divided road in Ireland with 2+1 lane configuration and wire-rope median barrier. Image credit: EuroRAP
A divided road in Ireland with 2+1 lane configuration and wire-rope median barrier. Image credit: EuroRAP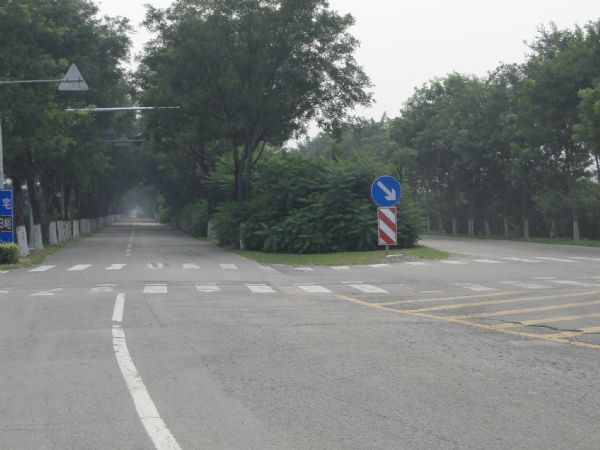 Divided road - China. Image credit: Greg Smith
Divided road - China. Image credit: Greg Smith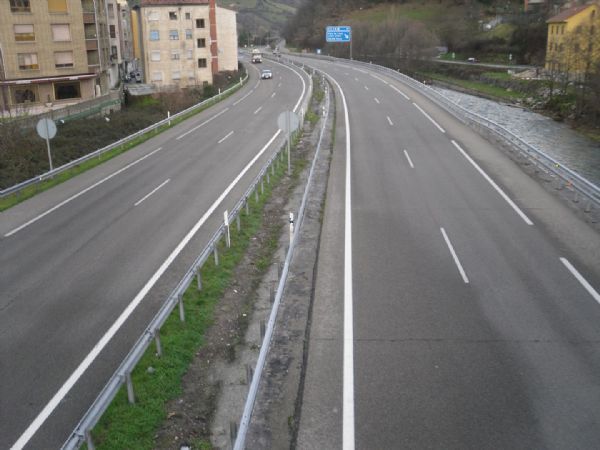 Duplication with median barrier in Asturias, Spain. Image credit: iRAP
Duplication with median barrier in Asturias, Spain. Image credit: iRAP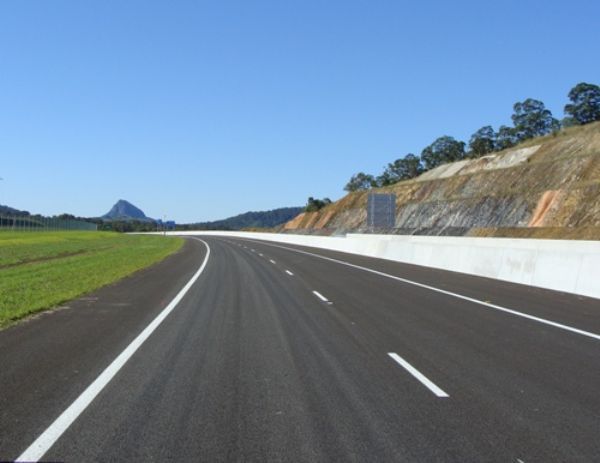 New duplicated section of the Bruce Highway (Cooroy to Curra), Queensland, Australia. Image credit: Luke Rogers, iRAP
New duplicated section of the Bruce Highway (Cooroy to Curra), Queensland, Australia. Image credit: Luke Rogers, iRAP










