



Bicycle Facilities
form an intuitive network that connects homes, schools, workplaces, recreation facilities and shopping precincts be well integrated with footpath crossings and bridges, and allow safe crossing of roads not require bicyclists to dismount frequently.
Increased safety for bicyclists. Increased use of bicycles (reduced road congestion). Associated health and environmental benefits that come with increased bicycle use.
On-road bicycle lanes are cheaper than off-road paths if shoulder sealing is not required. Traffic calming treatments, or narrow road sections such as bridges can force bicycles out into traffic, resulting in conflicts. Parked vehicles may also force bicycles out into traffic, and so parking enforcement is very important for the success of on-road lanes. Surface quality must be high or it will pose a safety risk. Bicycle lanes should be maintained properly to insure that bicyclists will prefer this to riding on the shoulder or in a vehicle lane of the roadway. Maintenance includes repairs to the pavement surface and vegetation clearance. Adequate sight distance must be provided around bends and at path intersections. This will also aid in improving personal security. Bicycle paths should be clear of obstructions. This includes keeping others such as vendors and adjacent land owners from encroaching on the path. Where an obstruction is necessary, it should be made obvious, and lines should be used to guide bicyclists safely past. Attention should be given to bicycle paths on downhill gradient and approaches to bicycle subways, particularly where less experienced users are expected. The roadside of bicycle facilities should be forgiving for errant cyclists as far as possible, particularly at critical sites such as the outside of sharp bends and the bottom of long gradients. Consideration should be given the suitable treatment of rigid objects or drops, especially if these lie close to bicycle facilities.
Treatment Summary
25-40% |
Case Studies
Related Images
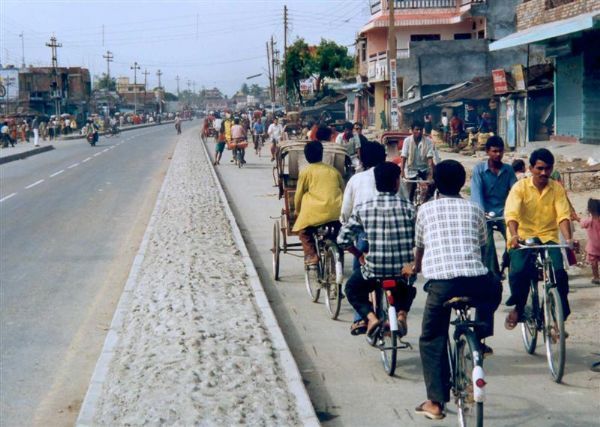

A dedicated off-road bicycle lane with >1m separation from traffic lane. Image credit: Unknown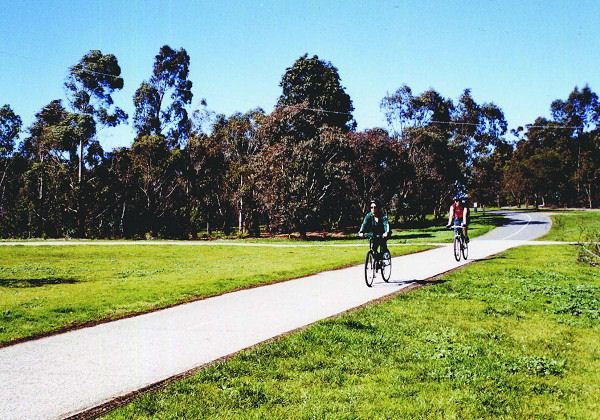 
Exclusive bicycle lane. Image credit: Unknown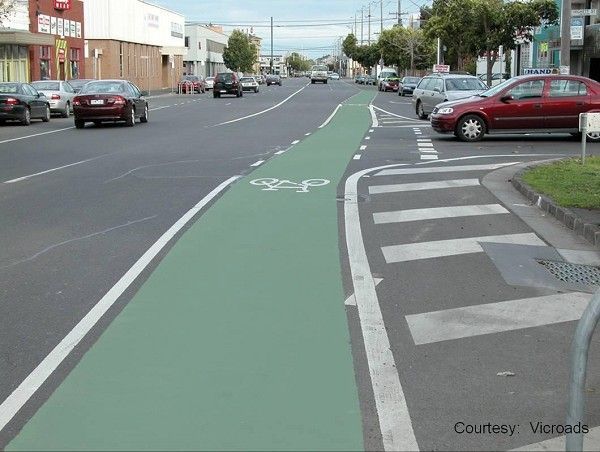 
On-road bicycle lane. Image credit: Unknown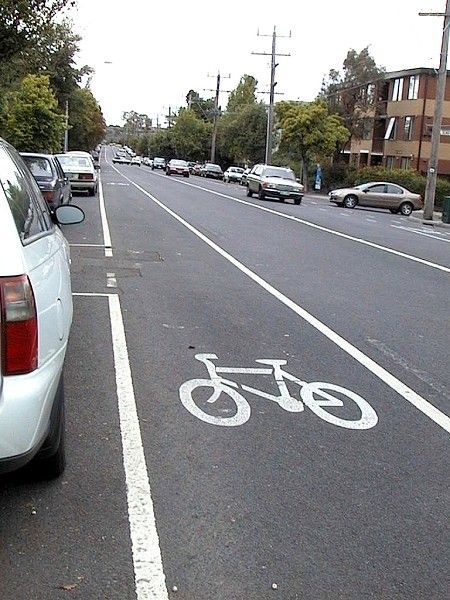 
On-road bicycle lane. Image credit: Unkown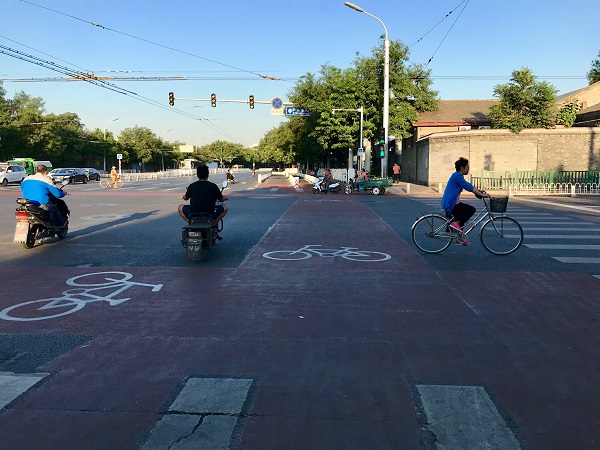 
Bicycle crossing in Beijing, China. Image credit: iRAP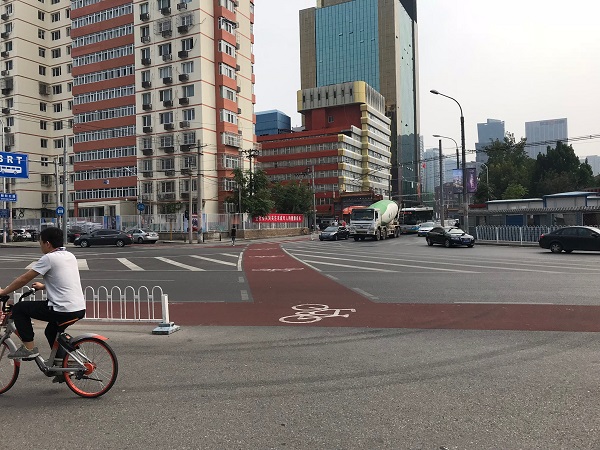 
Bicycle crossing in Beijing, China. Image Credit: Greg Smith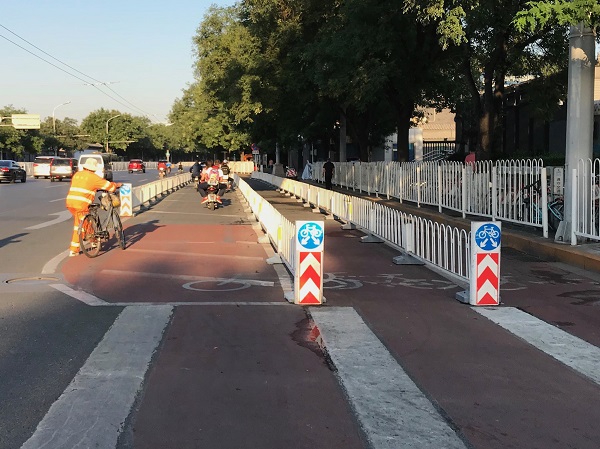 
Bicycle facility in Beijing, China. Image credit: iRAP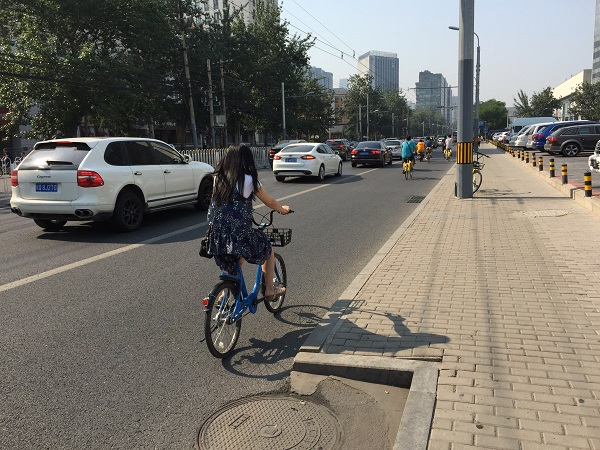 
Bicycle facility in Beijing, China. Image credit: iRAP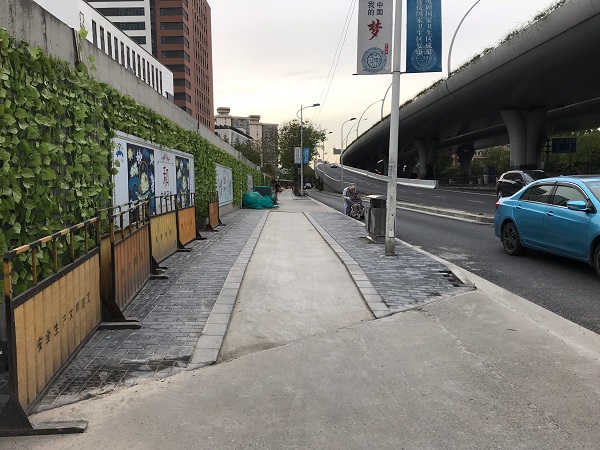 
Bicycle facility in Shanghai, China. Image Credit: iRAP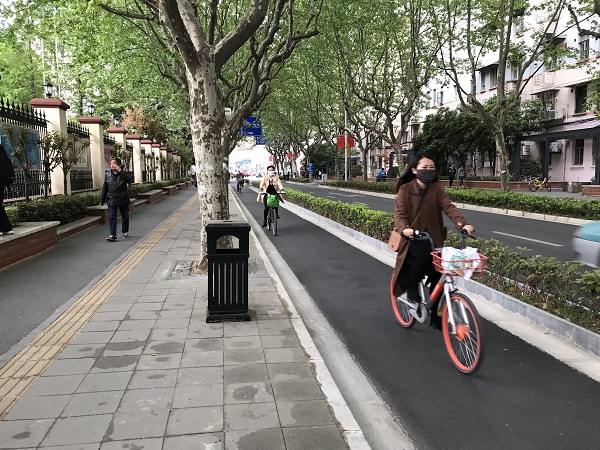 
Bicycle lane and sidewalk in China. Image credit: WRI 
Bicycle lane and sidewalk in Mexico. Image credit: Agustin Centeno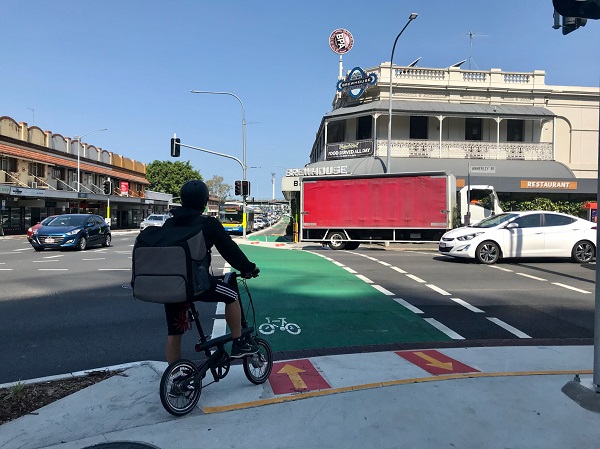 
Bicycle lane, Australia. Image credit: Unknown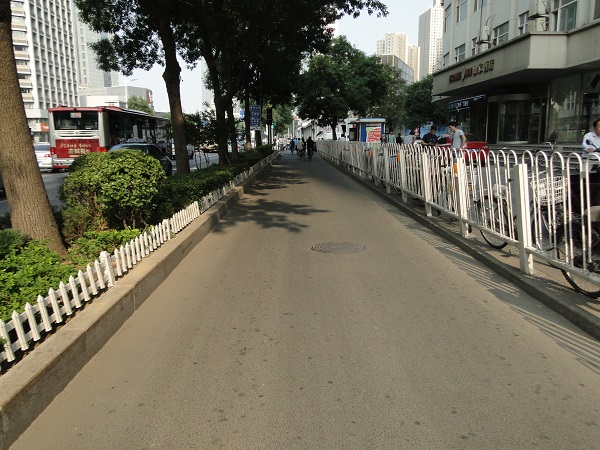 
Off-road bicycle lane. Image credit: iRAP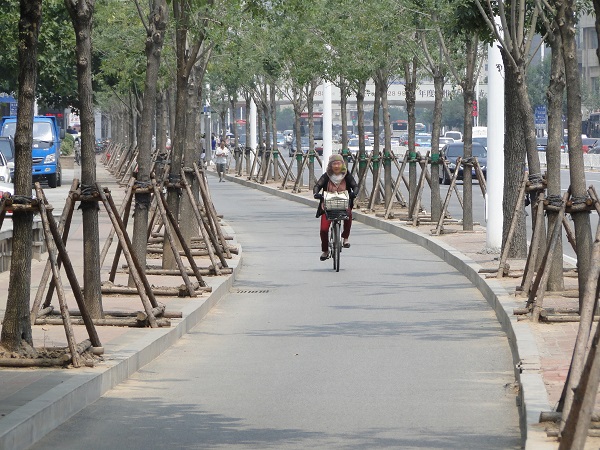 
Off -road bicycle lane in China. image credit: Greg Smith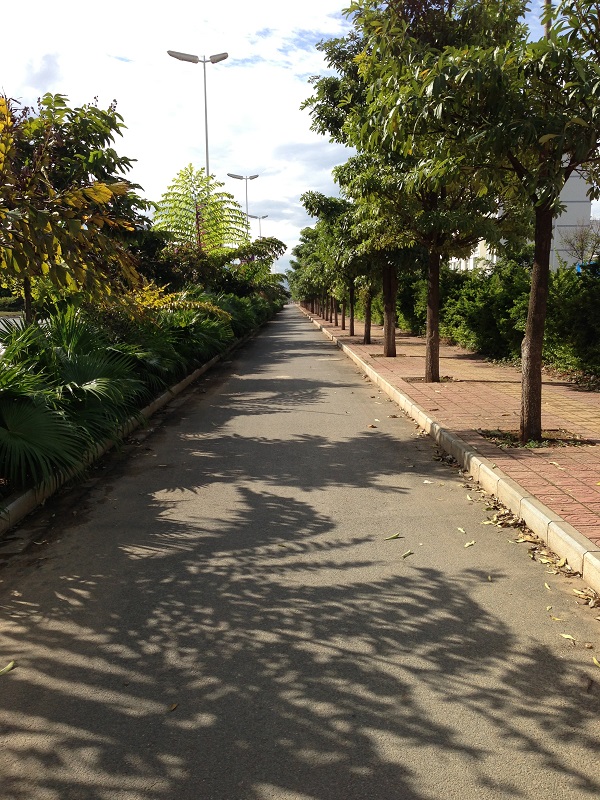 
Bicycle lane, China. Image credit: iRAP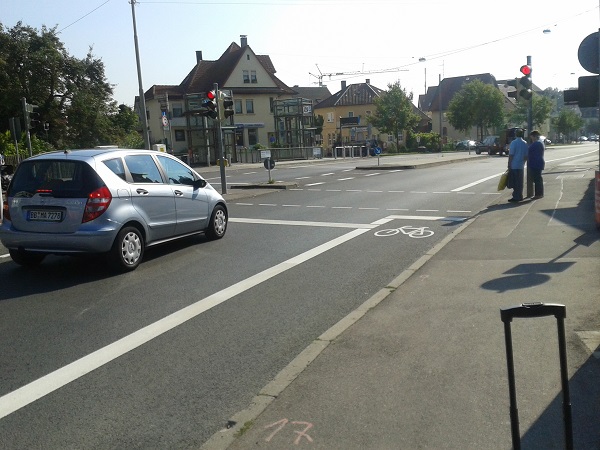 
On-road bicycle lane - Germany. Image credit: Alina Burlacu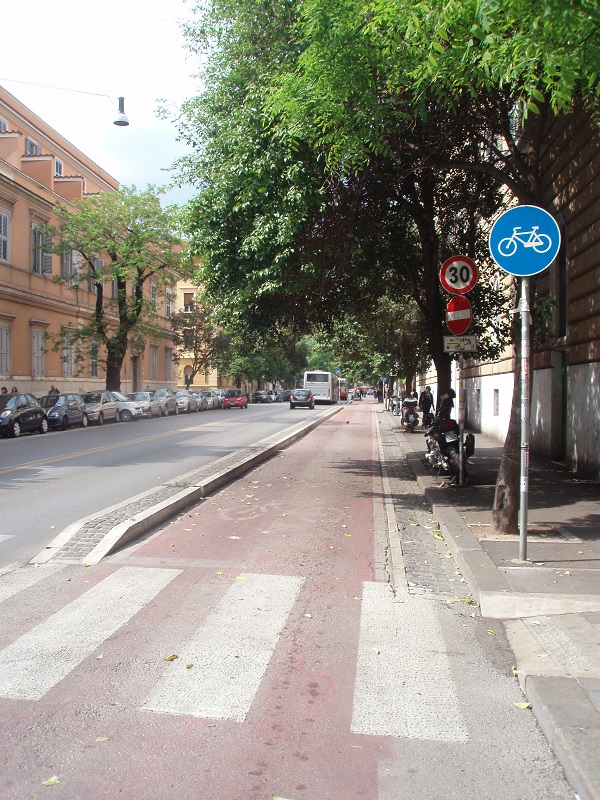 
Bicycle lane with <1m separation from traffic - Italy. Image credit: Alina Burlacu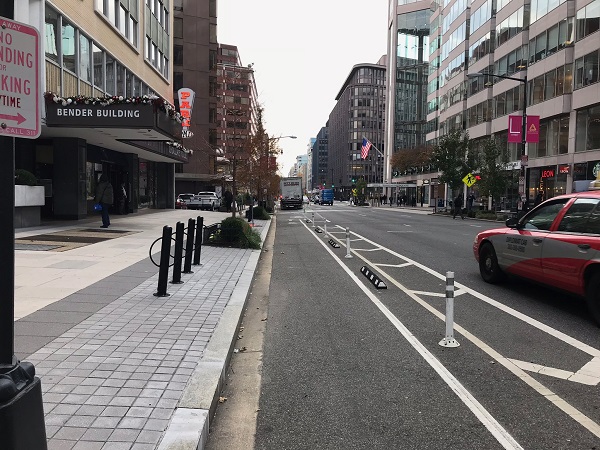 
Bicycle lane - USA. Image credit: Unknown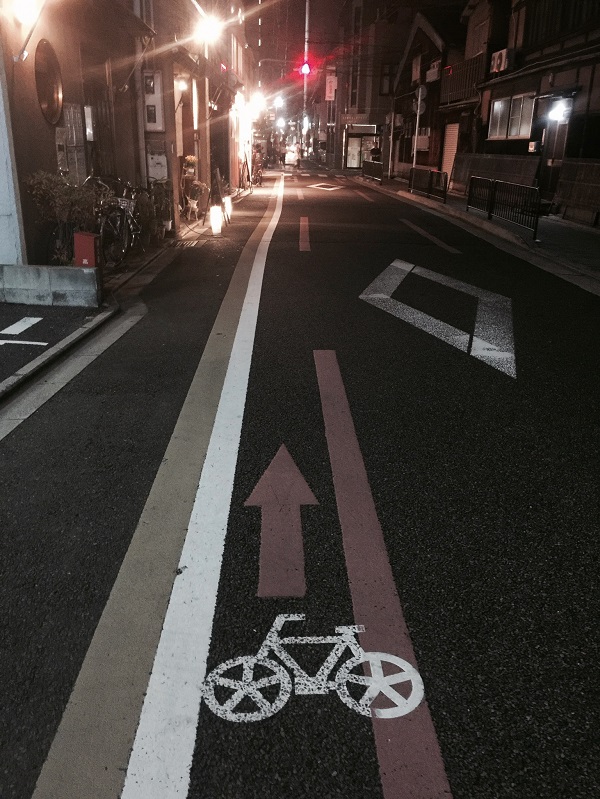 
Bicycle lane - Kyoto, Japan. Image Credit: iRAP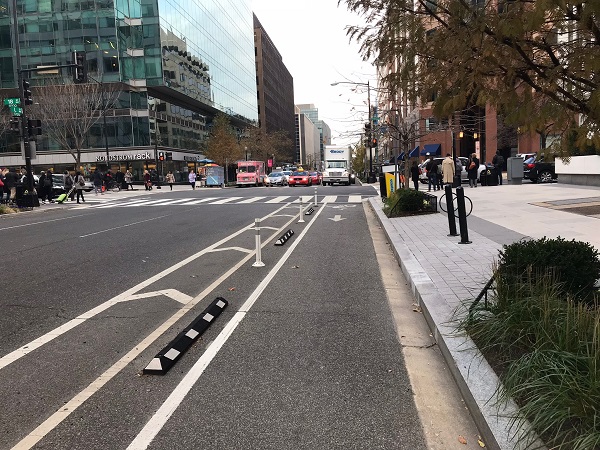 
Bicycle lane in Washington DC, USA. Image Credit: iRAP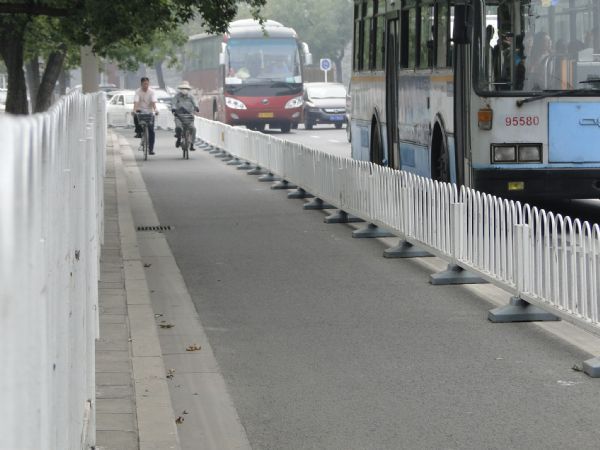 
Bicycle lane, Beijing, China. Image credit: Greg Smith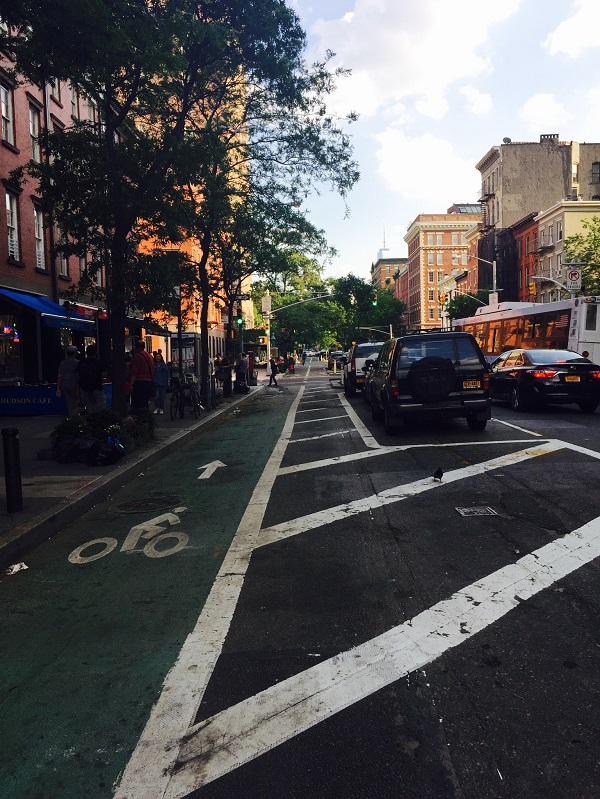 
Bicycle lanes, USA. Image credit: Unknown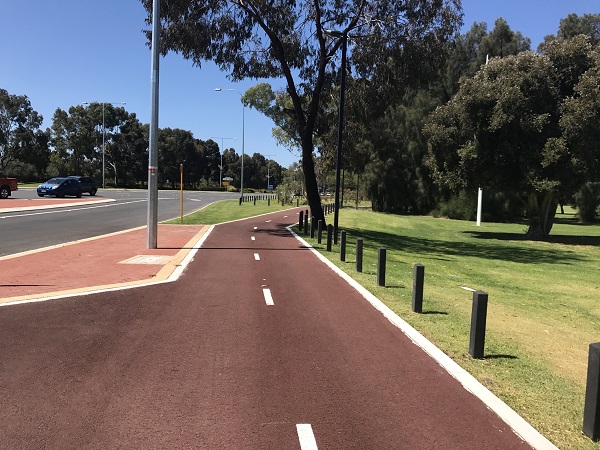 
Off-road bicycle path, Australia. Image credit: Alina Burlacu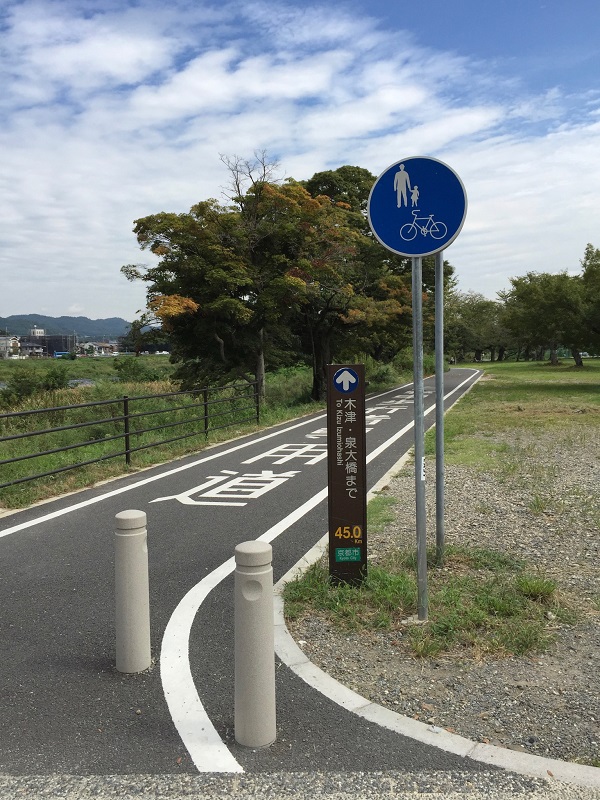 
Bicycle path, Japan. Image credit: Unknown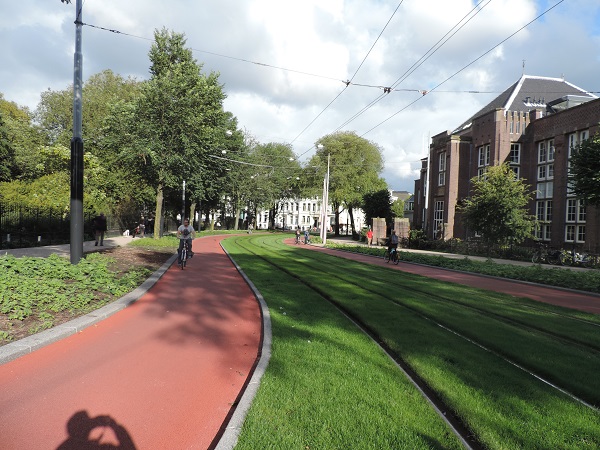 
Bicycle path, Netherlands. Image credit: Alina Burlacu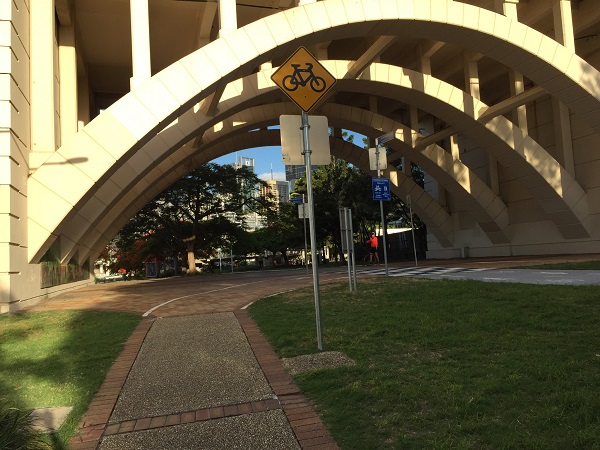 
Bicycle path, Brisbane, Australia. Image Credit: iRAP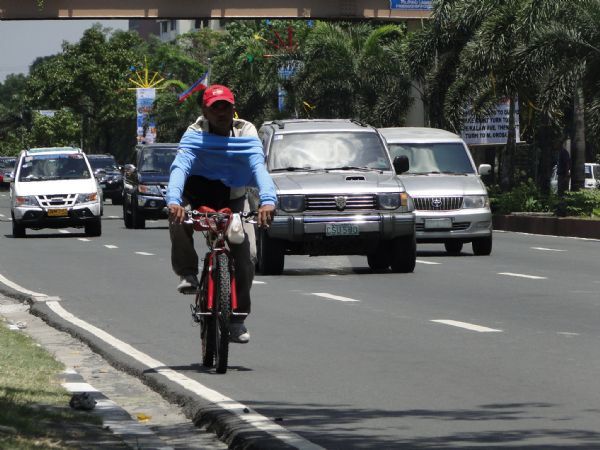 
Bicyclist - Roxas Blvd Manila Philippines. Image credit: Greg Smith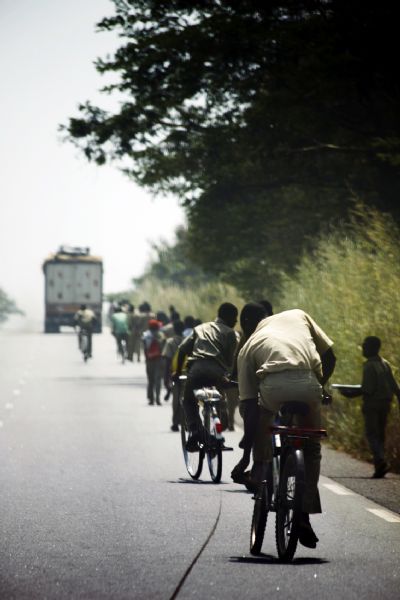 
Bicyclists in Africa. Image credit: iStock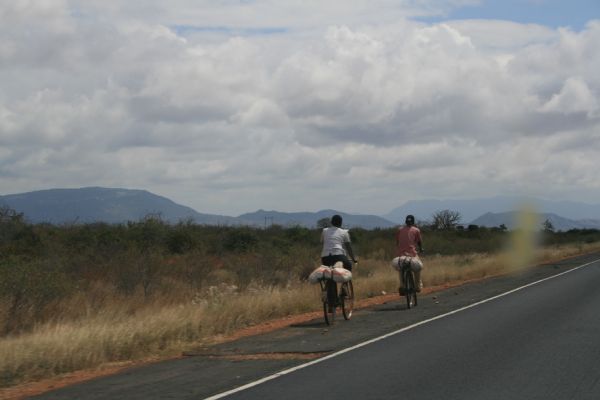 
Bicyclists in Kenya. Image credit: John Mumford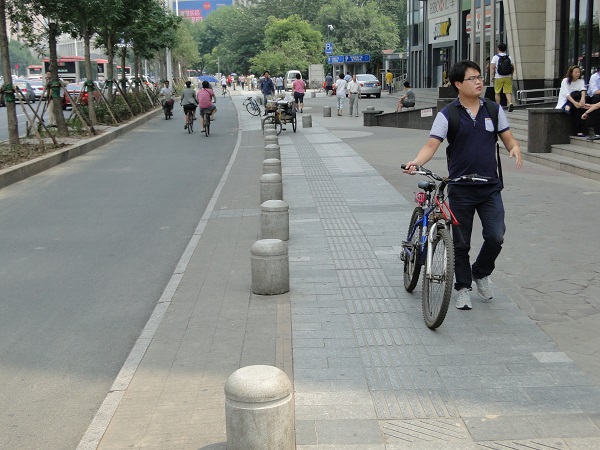 
Bollards protect a sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith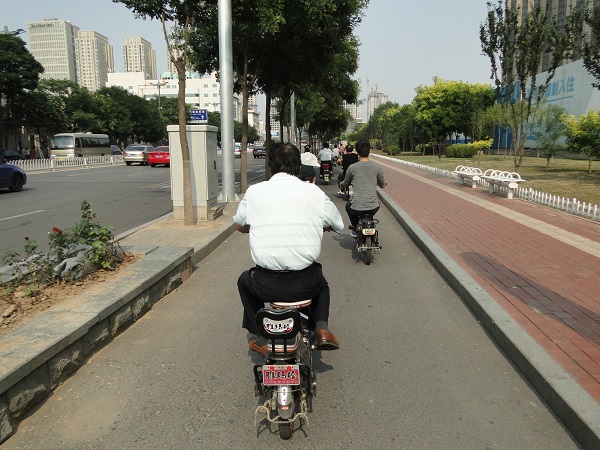 
E-bikes on a bicycle lane in China. Image credit: iRAP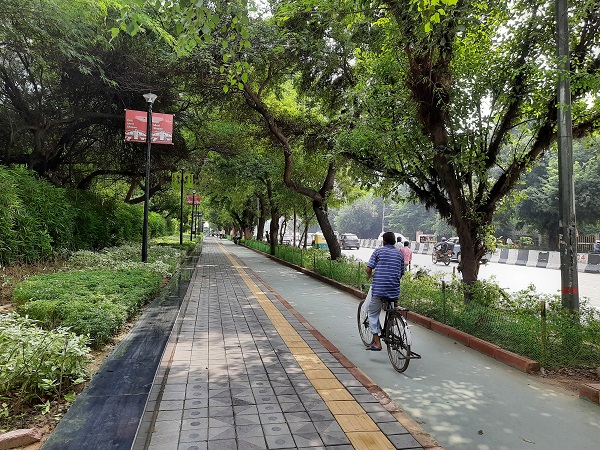 
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi India. Image credit: iRAP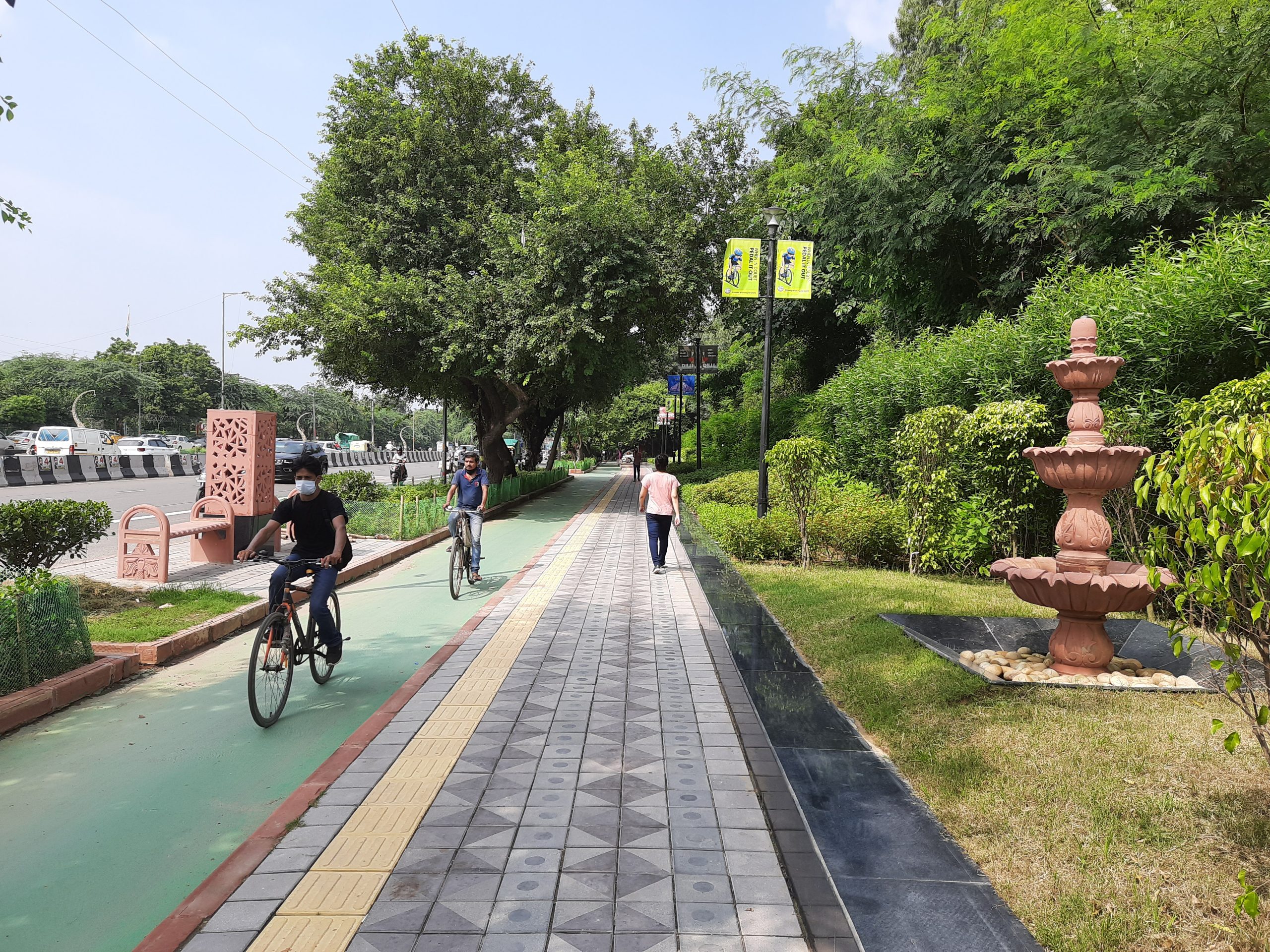 
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi India. Image credit: iRAP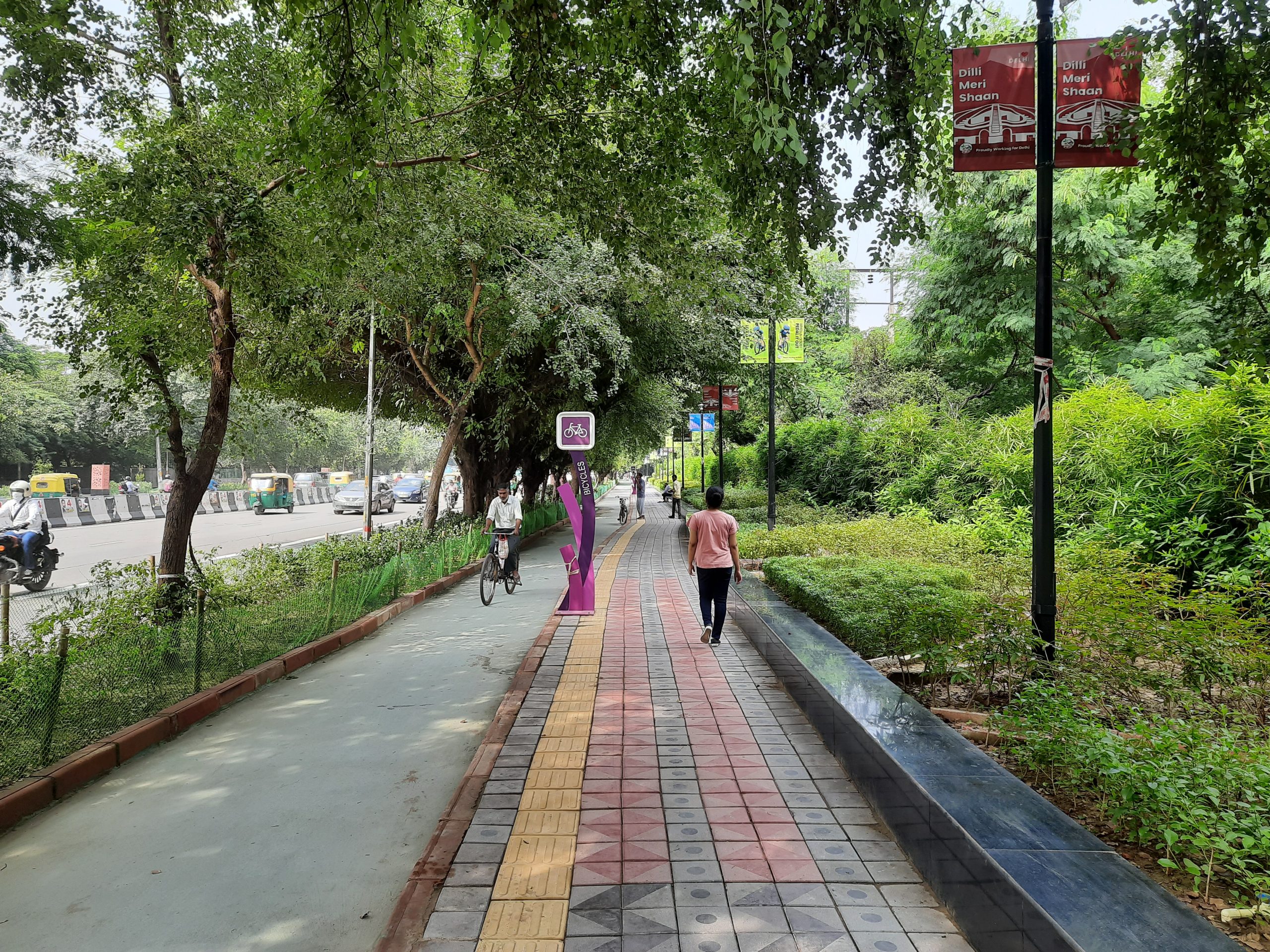 
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi, India. Image credit: iRAP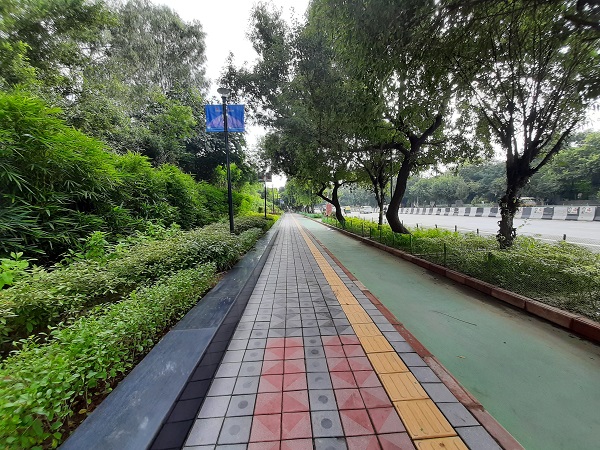 
Example of a road with a median and pedestrian refuge islands. Image credit: https://safety.fhwa.dot.gov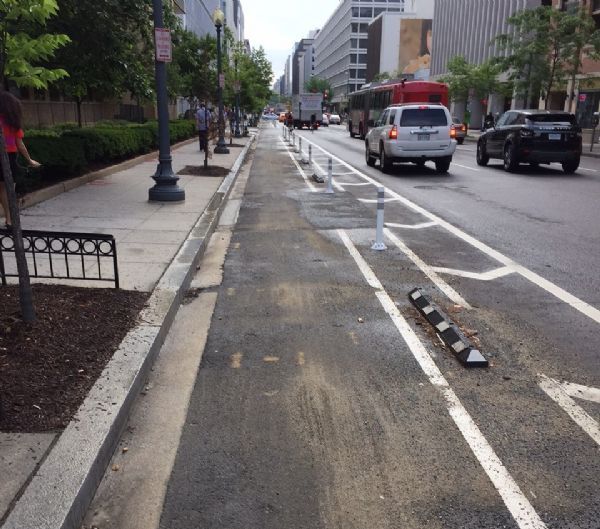 
An on-road bicycle lane in US. Image credit: Greg Smith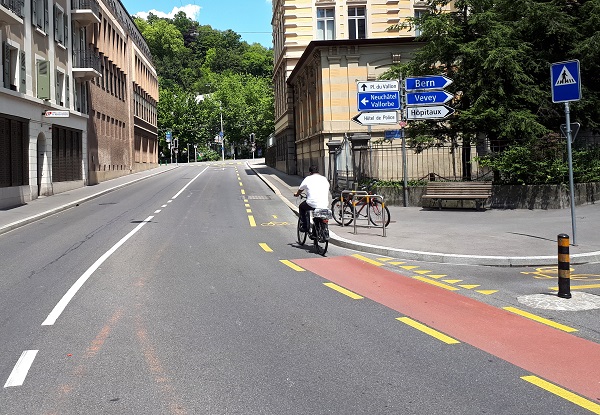 
On-road dedicated bicycle lane. Image credit: Alain Rouiller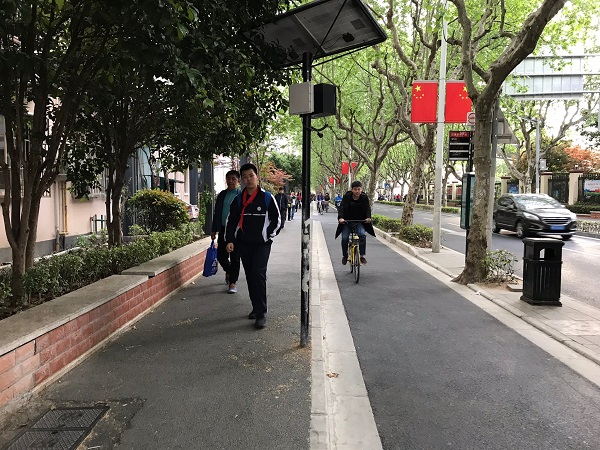 
Pedestrian and bicycle facilities in Shanghai. Image credit: Unknown 
Pedestrian refuges, bicycle lanes, delineation and one-way road treatment. Image credit: Google Maps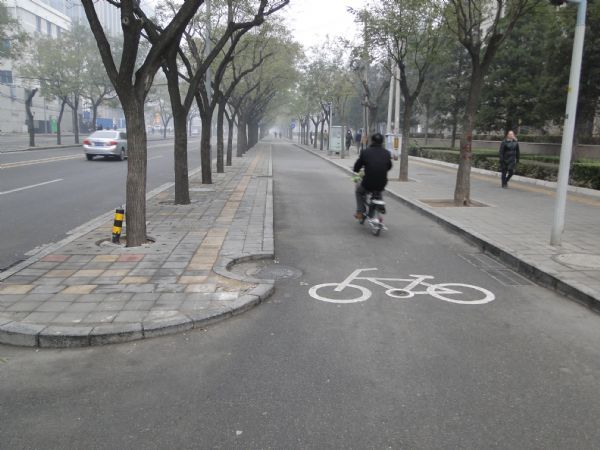 
Protected bicycle lane in China. Image credit: Greg Smith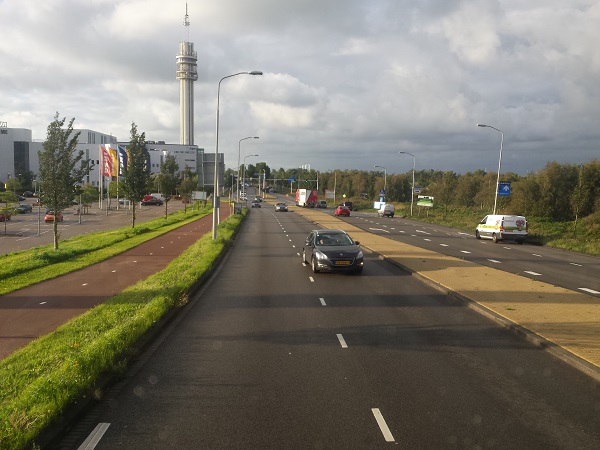 
Separated bicycle path - Netherlands. Image credit: Alina Burlacu 
Urban road at a multimodal transport hub with sidewalks, bicycle lanes, median and pedestrian crossing in China. Image credit: Tianjin Urban Construction Design Institute 
Traffic calming and pedestrian crossing. Photo credit: RdA Suisse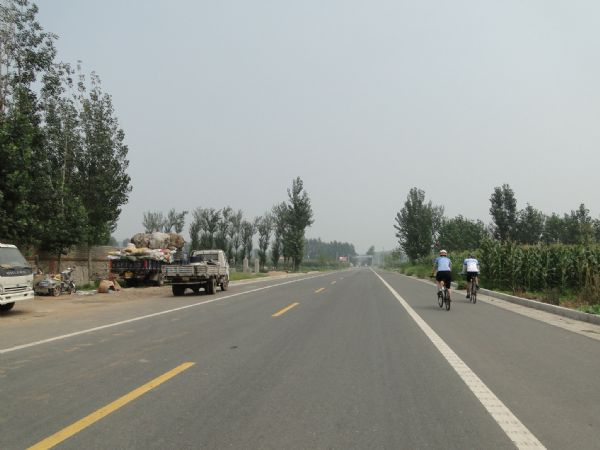 
Wide sealed shoulder bicycle lane, China. Image credit: Greg Smith










