



Pedestrians
At some point in every journey on the road everyone is a pedestrian. Apart from walking, pedestrians may also use wheelchairs, motorized scooters, walkers, canes, skateboards, and roller blades. People who are running, jogging or hiking, or standing on the road are also pedestrians.
Travel as a pedestrian is an active and sustainable form of transport. In some cases, travel as a pedestrian may comprise the entire journey, in others it may comprise just part of the journey, such as walking to and from bus stops. There are many reasons that people want to travel as pedestrians, such as to go to school or work, to access other forms of transport, to visit markets or friends and family, and for recreation.
Pedestrians are vulnerable road users. In many countries, collisions with pedestrians are a leading cause of death and injury. In some countries, over half of all road deaths are caused by collisions between vehicles and pedestrians.
High quality pedestrian environments are conducive to safe and sustainable pedestrian activity. Where traffic speeds are high, footpaths are missing or inaccessible, or where pedestrian crossings are inadequate, there is either less pedestrian activity or there is higher numbers of pedestrian deaths and serious injuries when people have no choice but to walk. High quality pedestrian environments are also essential for public transport.
Some populations may be at a higher risk of pedestrian crashes. Children and the elderly are often overrepresented in road crashes and so pedestrian environments around schools and where there are elderly people need special attention.
Case Studies
| Name | Cost rating | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Central Hatching | Low | 10 – 25% |
| Intersection – Signalise | Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Parking Improvements | Low to Medium | 10 – 25% |
| Pedestrian Crossing – Grade Separation | High | 60% or more |
| Pedestrian Crossing – Signalised | Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Pedestrian Crossing – Unsignalised | Low | 25 – 40% |
| Pedestrian Fencing | Low | 25 – 40% |
| Pedestrian Footpath | Low to Medium | 40 – 60% |
| Pedestrian Refuge Island | Low to Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Regulate Roadside Commercial Activity | Low to Medium | 10 – 25% |
| Restrict/Combine Direct Access Points | Medium to High | 25 – 40% |
| School Zones | Low to Medium | 10 – 25% |
| Service Road | High | 25 – 40% |
| Paved Shoulder | Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Sight Distance (obstruction removal) | Low to Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Skid Resistance | Low to Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Speed Management | Medium | 25 – 40% |
| Street Lighting | Medium | 10 – 25% |
| Traffic Calming | Medium to High | 25 – 40% |
| Name | Cost rating | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) | – | – |
| Name | Cost rating | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Addressing Alcohol and Other Drugs | – | – |
| Education | – | – |
| Emergency Response | – | – |
| Enforcement | – | – |
| Publicity | – | – |
| Safe Speed | – | – |
Related Images
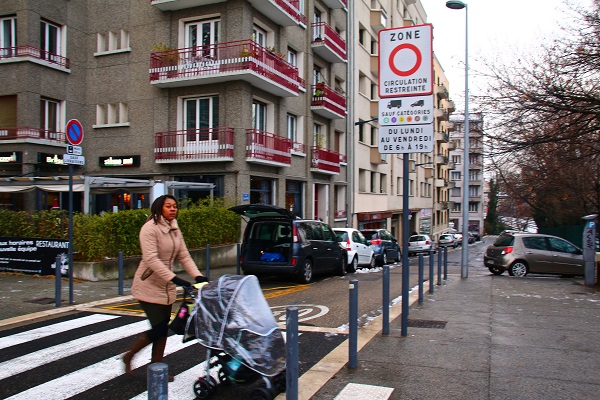 A mother crossing the road with a stroller. Photo credit: RdA Suisse
A mother crossing the road with a stroller. Photo credit: RdA Suisse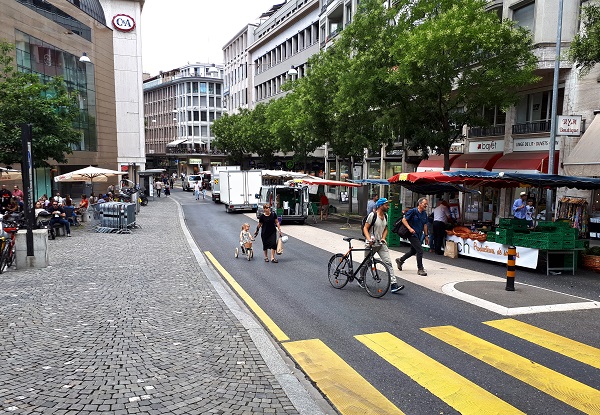 Pedestrians crossing a slow speed road. Photo credit: RdA Suisse
Pedestrians crossing a slow speed road. Photo credit: RdA Suisse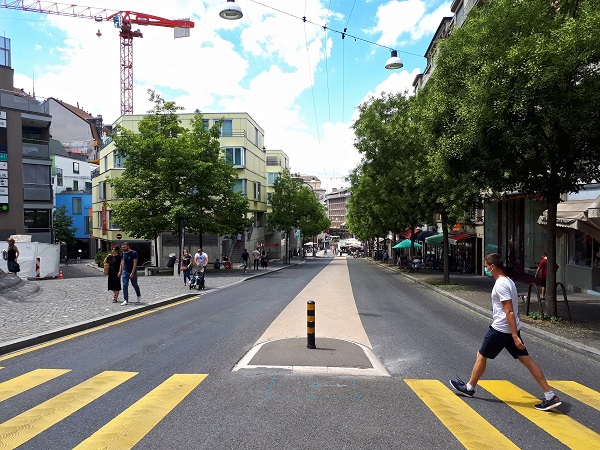 A pedestrian crossing a road with a pedestrian crossing and median. Photo credit: RdA Suisse
A pedestrian crossing a road with a pedestrian crossing and median. Photo credit: RdA Suisse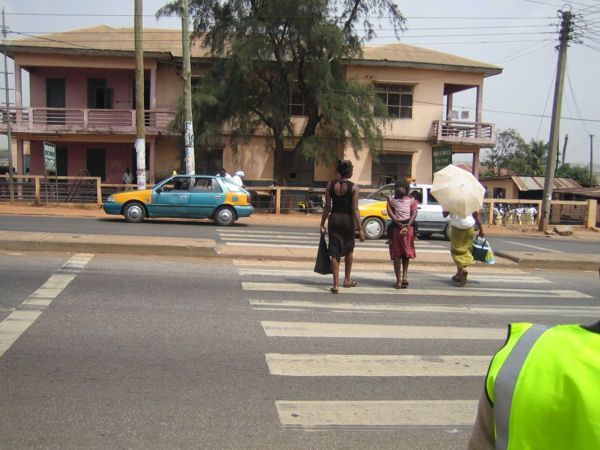 A pedestrian crossing facility with refuge island in Ghana. Image credit: John Fletcher
A pedestrian crossing facility with refuge island in Ghana. Image credit: John Fletcher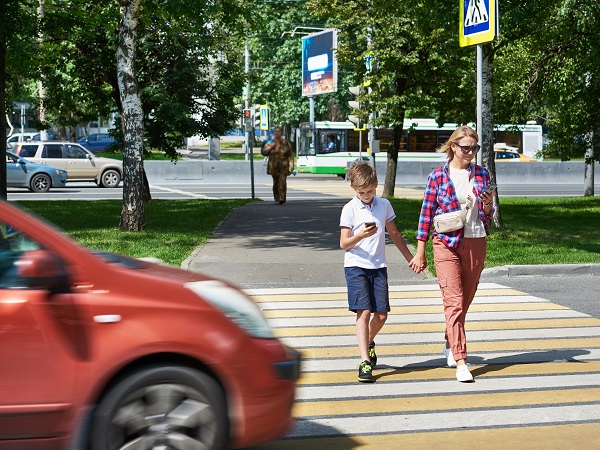 A potential crash involving mother and child pedestrians. Image credit: iStock
A potential crash involving mother and child pedestrians. Image credit: iStock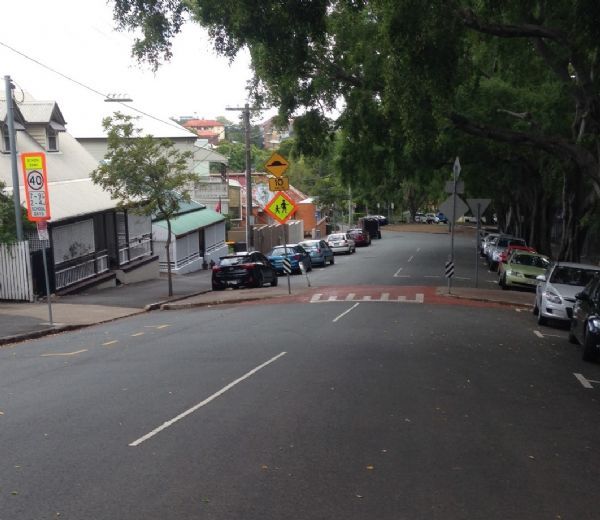 A raised pedestrian crossing with kerb build-out in a school zone in Brisbane, Australia. This is an effective traffic calming measure whilst providing a safe place to cross. Image credit: Luke Rogers
A raised pedestrian crossing with kerb build-out in a school zone in Brisbane, Australia. This is an effective traffic calming measure whilst providing a safe place to cross. Image credit: Luke Rogers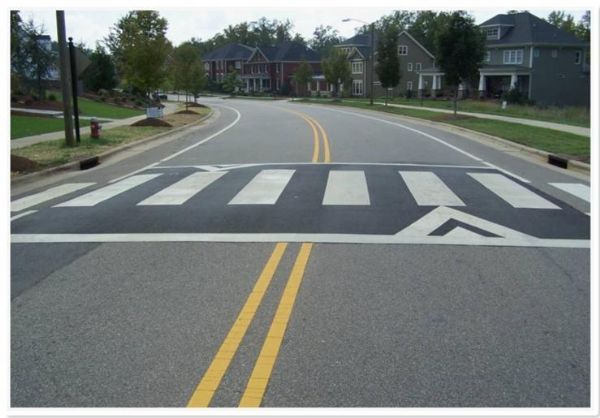 A raised pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Unknown
A raised pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Unknown A signalised pedestrian crossing in Oviedo, Spain. Image credit: iRAP
A signalised pedestrian crossing in Oviedo, Spain. Image credit: iRAP Bollards protect a sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith
Bollards protect a sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith Busy pedestrian crossing. Image credit: iStock
Busy pedestrian crossing. Image credit: iStock A child sits on the road. Image credit: Unknown
A child sits on the road. Image credit: Unknown Children crossing a road. Image credit: iStock
Children crossing a road. Image credit: iStock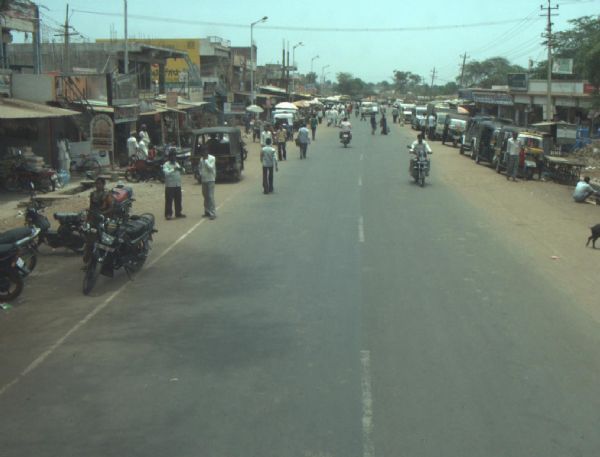 Road passing through a rural town in India. The section has commercial road side activities and high presence of pedestrians. Image credit: iRAP
Road passing through a rural town in India. The section has commercial road side activities and high presence of pedestrians. Image credit: iRAP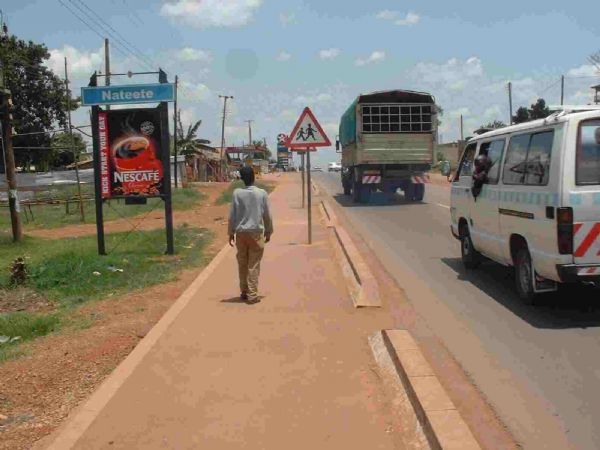 A low-cost and easy to implement pedestrian footpath in Kampala, Uganda. Even simple footpaths like this one have the potential to significantly improve safety for pedestrians. Image credit: Allan Jones
A low-cost and easy to implement pedestrian footpath in Kampala, Uganda. Even simple footpaths like this one have the potential to significantly improve safety for pedestrians. Image credit: Allan Jones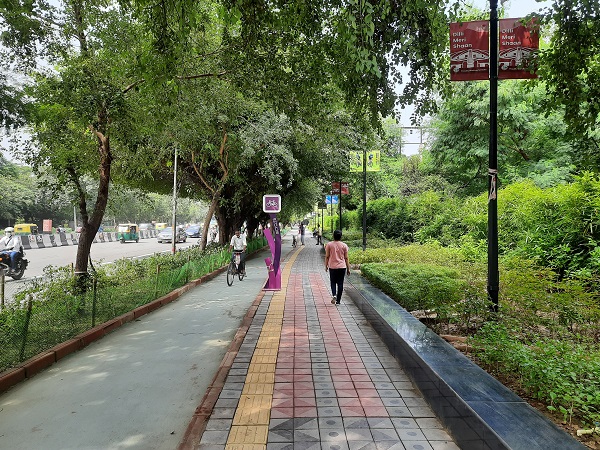 Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi, India. Image credit: iRAP
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi, India. Image credit: iRAP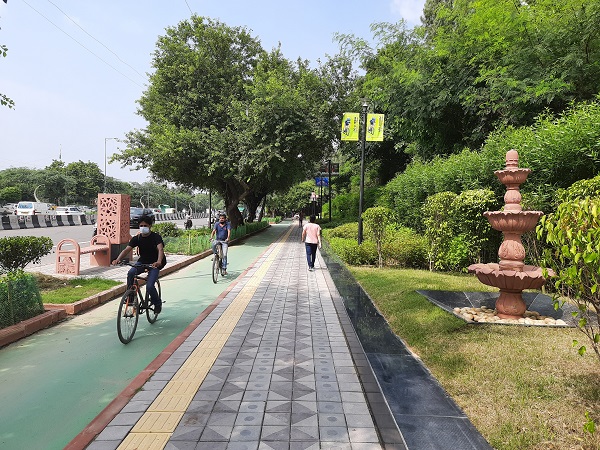 Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi India. Image credit: iRAP
Exclusive bicycle lane and pedestrian footpath in New Delhi India. Image credit: iRAP Pedestrians in India. Image Credit: iStock
Pedestrians in India. Image Credit: iStock Informal sidewalk in Uzbekistan. Image credit: Anvar Matkarimov
Informal sidewalk in Uzbekistan. Image credit: Anvar Matkarimov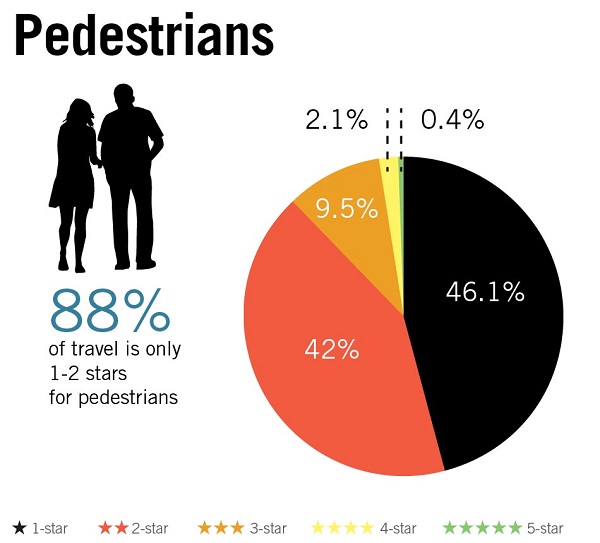 Pedestrian Star Ratings by road user type based on a 358,000km sample of roads across 54 countries. Image credit: iRAP
Pedestrian Star Ratings by road user type based on a 358,000km sample of roads across 54 countries. Image credit: iRAP Children walk along a road. Image credit: N Zwarg
Children walk along a road. Image credit: N Zwarg Signalised pedestrian crossing in Kazakhstan. Image credit: Anvar Matkarimov
Signalised pedestrian crossing in Kazakhstan. Image credit: Anvar Matkarimov Children crossing a road. Image credit: iStock
Children crossing a road. Image credit: iStock Long pedestrian bridge with limited access in the Philippines. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Long pedestrian bridge with limited access in the Philippines. Image credit: Alina Burlacu Marked pedestrian crossing facility (Zebra marking). Image credit: Alain Rouiller
Marked pedestrian crossing facility (Zebra marking). Image credit: Alain Rouiller Pedestrian crossing - Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrian crossing - Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrian crossing in New York USA. Image Credit: iRAP
Pedestrian crossing in New York USA. Image Credit: iRAP Pedestrian crossing in Tokyo, Japan. Image Credit: iRAP
Pedestrian crossing in Tokyo, Japan. Image Credit: iRAP Pedestrian Fencing in China. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrian Fencing in China. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrian footbridge - Roxas Blvd Manila, Philippines. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrian footbridge - Roxas Blvd Manila, Philippines. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrian footover bridge in India. Image credit: iRAP
Pedestrian footover bridge in India. Image credit: iRAP Pedestrian refuge island (overrunable) in Kathmandu. Image credit: Allan Jones
Pedestrian refuge island (overrunable) in Kathmandu. Image credit: Allan Jones Pedestrians in London, England. Image Credit: iRAP
Pedestrians in London, England. Image Credit: iRAP Pedestrians in Tianjin, China. Image Credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians in Tianjin, China. Image Credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians cross busy multilane road underneath a pedestrian bridge in China. Image Credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians cross busy multilane road underneath a pedestrian bridge in China. Image Credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians cross a busy road in India. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians cross a busy road in India. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians in China. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians in China. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians in Ha Noi, Viet Nam. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians in Ha Noi, Viet Nam. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians in India. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians in India. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians in Tanzania. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Pedestrians in Tanzania. Image credit: Alina Burlacu Pedestrian on a city road in Indonesia. Image credit: iRAP
Pedestrian on a city road in Indonesia. Image credit: iRAP Pedestrians walking on informal footpath along a rural road in India. Image credit: iStock
Pedestrians walking on informal footpath along a rural road in India. Image credit: iStock Pedestrians wait for a bus in Bangladesh. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians wait for a bus in Bangladesh. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians walk along a road in Bangladesh. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians walk along a road in Bangladesh. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians walk along a road in India. Image credit: Alina Burlacu
Pedestrians walk along a road in India. Image credit: Alina Burlacu Pedestrians walk on the road because of an obstructed sidewalk, China. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians walk on the road because of an obstructed sidewalk, China. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians walking in the road despite the presence of a footpath in New Delhi, India. Image credit: Greg Smith
Pedestrians walking in the road despite the presence of a footpath in New Delhi, India. Image credit: Greg Smith Pedestrians in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Image Credit: iRAP
Pedestrians in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Image Credit: iRAP Pedestrians in Tianjin, China. Image Credit: iRAP
Pedestrians in Tianjin, China. Image Credit: iRAP Pedestrians in Tokyo, Japan. Image Credit: iRAP
Pedestrians in Tokyo, Japan. Image Credit: iRAP People walk along a busy road with no sidewalk. Image credit: iStock
People walk along a busy road with no sidewalk. Image credit: iStock Physical channelisation (and planting) under the flyover to provide a safe refuge for pedestrians to cross the road in two stages. Image credit: Gladys Frame
Physical channelisation (and planting) under the flyover to provide a safe refuge for pedestrians to cross the road in two stages. Image credit: Gladys Frame Public transport in Bangladesh. Image credit: Greg Smith
Public transport in Bangladesh. Image credit: Greg Smith Raised (table-top type) pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Alain Rouiller
Raised (table-top type) pedestrian crossing facility. Image credit: Alain Rouiller Raised pedestrian crossing facility in China. Image credit: Unknown
Raised pedestrian crossing facility in China. Image credit: Unknown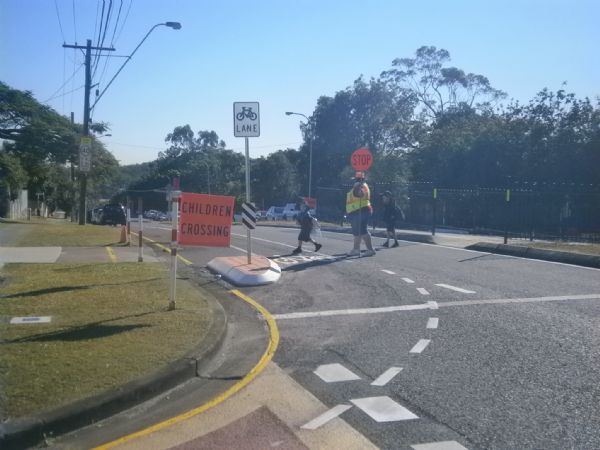 School Zone crossing supervisor in Australia. Image credit: Unknown
School Zone crossing supervisor in Australia. Image credit: Unknown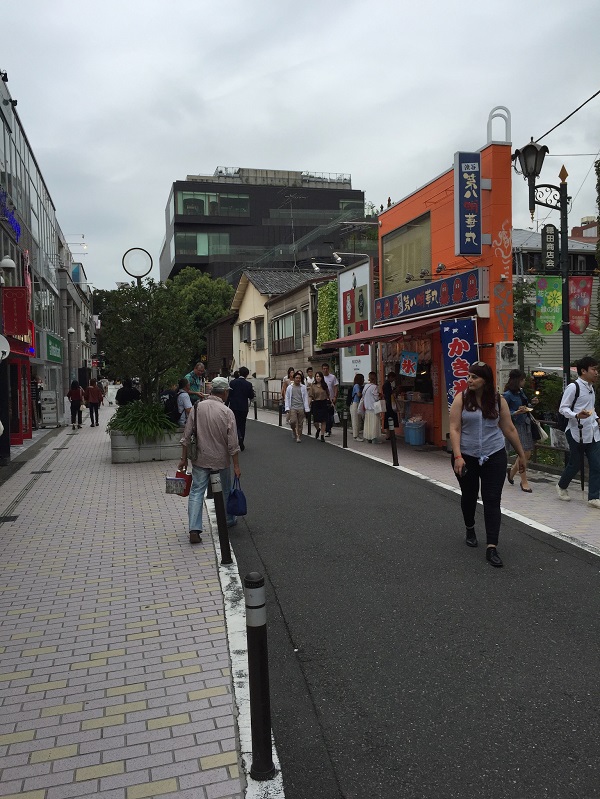 Shared Street in Tokyo. Image Credit: iStock
Shared Street in Tokyo. Image Credit: iStock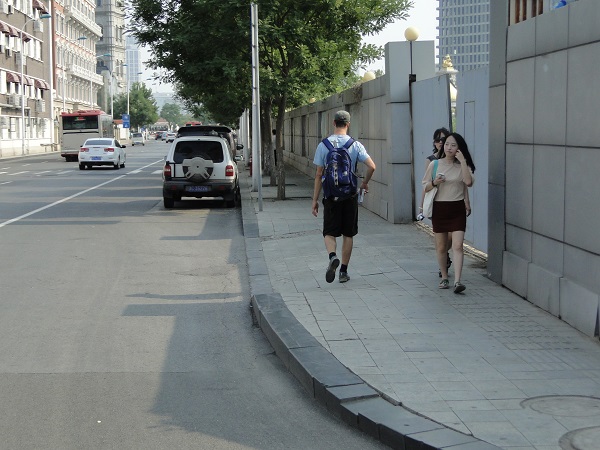 A sidewalk in China. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers
A sidewalk in China. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers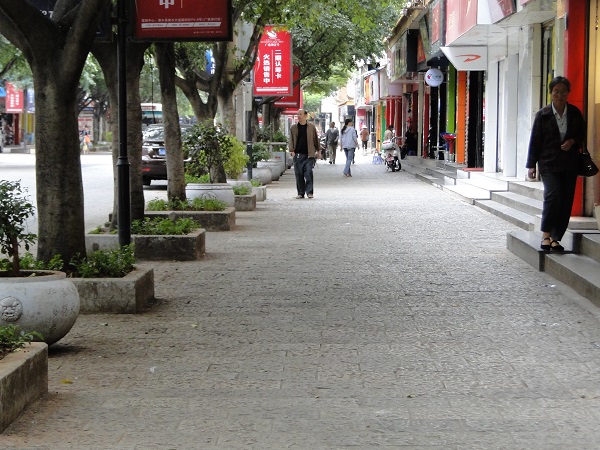 A sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith
A sidewalk in China. Image credit: Greg Smith A sidewalk in Shanghai, China. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers
A sidewalk in Shanghai, China. Image credit: Monica Olyslagers Simple pedestrian footpath in a semi-urban area of New Zealand. Image credit: Greg Smith
Simple pedestrian footpath in a semi-urban area of New Zealand. Image credit: Greg Smith Narrow sidewalk in Japan. Image credit: Michael Martin
Narrow sidewalk in Japan. Image credit: Michael Martin Pedestrians crossing the road, with traffic calming and pedestrian crossing. Image credit: RdA Suisse
Pedestrians crossing the road, with traffic calming and pedestrian crossing. Image credit: RdA Suisse








